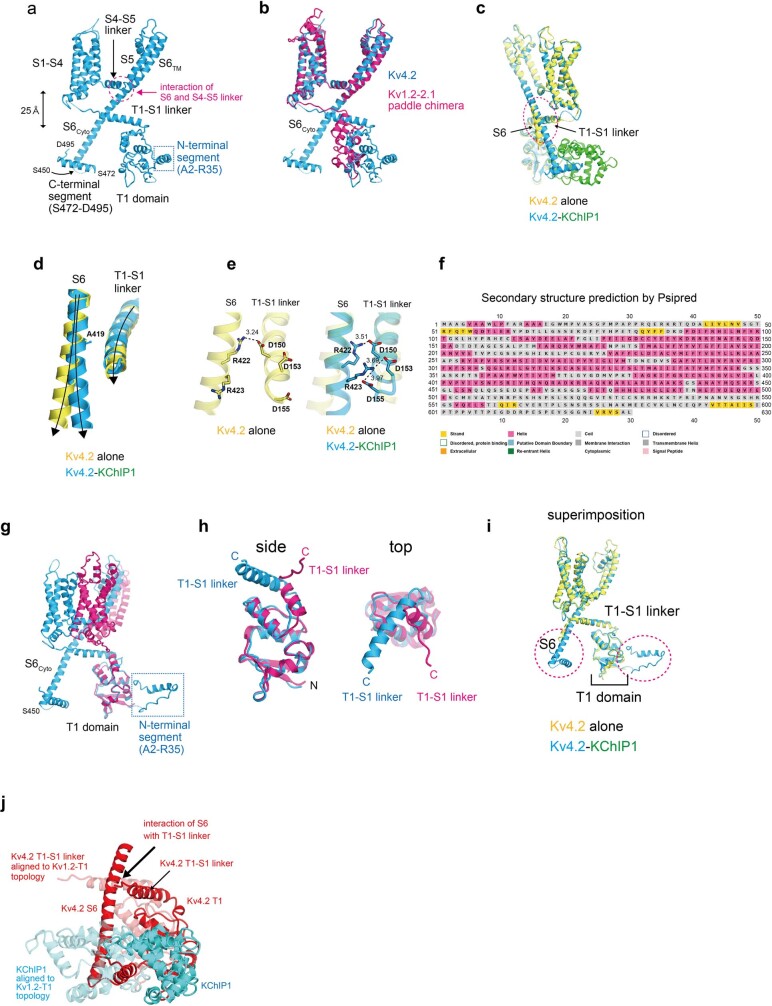
Extended Data Fig. 5. Structures of the Kv4.2 α-subunit protomer in the presence and absence of KChIP1 and comparison with the Kv1.2-2.1 chimera.
a. Structure of the Kv4.2 α-subunit protomer in the Kv4.2–KChIP1 complex. The T1 domain is located beneath the transmembrane domain at a distance of 25 Å. Note that the transmembrane S6TM helix further extends toward the intracellular region, as indicated by the S6cyto (to S450) and C-terminal segment (S472-D495). Residues 496-630 are disordered and most of this region is predicted to lack secondary structure (f). b. Structural comparison of Kv4.2–KChIP1 with the Kv1.2-2.1 chimera, superimposed by transmembrane domains. The overall structure of the transmembrane domain of Kv4.2 is similar to the structures of the Kv1.2-2.1 paddle chimera. Note that the two T1 domains do not superimpose on each other. The Kv1.2-2.1 chimera does not have an intracellular S6 helix. c. The intracellular S6 helix of Kv4.2 alone bends at the interface on the T1-S1 linker (dashed ellipse) and is subsequently disordered. In contrast, the S6 helix of Kv4.2–KChIP1 complex extends straight toward KChIP1. d. Close-up view of the superimposed image in the dashed ellipse in (c). The intracellular S6 of Kv4.2 starts bending from A419 and extend away from the T1-S1 linker in the Kv4.2 alone. However, it keeps a close distance to T1-S1 linker without bending in the Kv4.2–KChIP1 complex. e. In the Kv4.2–KChIP1 complex, the intracellular S6 and T1-S1 linker interact via electrostatic interactions (right). In the Kv4.2 alone, the intracellular S6 largely dissociates from the T1-S1 linker (left). f. Prediction of the secondary structure of Kv4.2 by PSIPRED. Most of the region consisting of residues 496-630 is predicted to lack secondary structure. g. Structural comparison of Kv4.2–KChIP1 with the Kv1.2-2.1 chimera, superimposed by the T1 domains. The two T1 domains fit very well, but the transmembrane domains do not. h. Different directions of the C-terminal part of T1 domains, resulting in distinct topologies between Kv4.2 and the Kv1.2-2.1 chimera. Side (left) and top (right) views of the T1 domains are shown. i. Superimposition of the protomers of Kv4.2 alone and the Kv4.2-KChIP1 complex shows that the T1 domains of Kv4.2 overlap and retain the same topology in the presence and absence of KChIP1. j. When the Kv4.2-T1 domain is aligned with the Kv1.2-T1 topology (shown by translucent structure), the Kv4.2 S6 helix clashes with KChIP1 and does not interact with a T1-S1-linker.