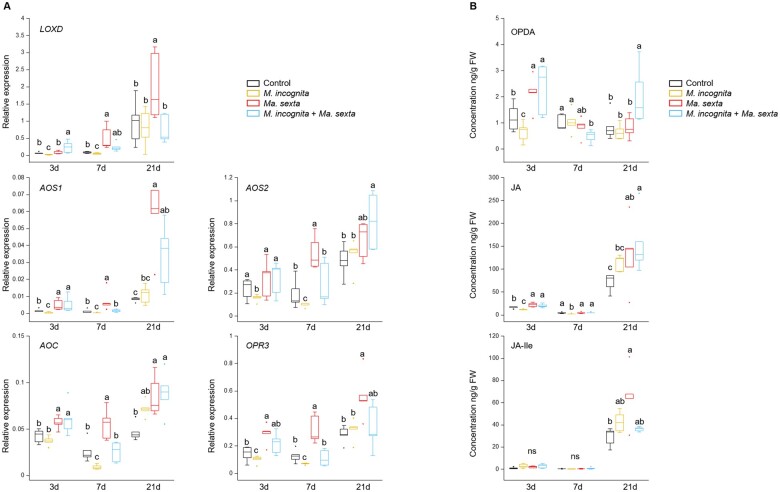
Figure 2.
Ma. sexta leaf herbivory antagonizes the repression of the 13-LOX oxylipin pathway triggered by M. incognita in tomato roots. A, Expression levels of the 13-LOX biosynthesis marker genes LOXD (LIPOXYGENASE D), AOS1 (ALLENE OXIDE SYNTHASE 1), AOS2 (ALLENE OXIDE SYNTHASE 2), AOC (ALLENE OXIDE CYCLASE), and OPR3 (12-OXOPHYTODIENOIC ACID REDUCTASE 3) and (B) root levels of OPDA, JA, and JA-Ile. Gene expression and metabolite contents were analyzed in roots of plants that were challenged with M. incognita or Ma. sexta alone or in combination, and in unchallenged control plants. Gene expression and metabolite contents were analyzed 3, 7, and 21 d after M. incognita inoculation. Box plots represent the IQR, the bisecting line represents the median, the whiskers represent 1.5 times the IQR, the dots represent outlier points, and the data are from five individual plants. In (A), the results are normalized to SlEF gene expression levels. At each specific time point, different letters indicate differences between treatments (ANOVA, Tukey’s test; P ≤ 0.05). ns: not significant.