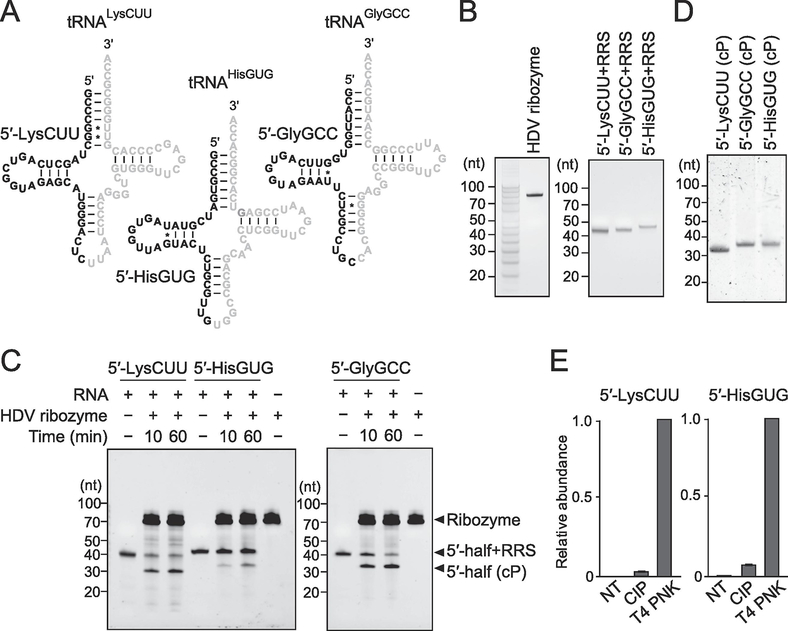
Figure 1. In vitro production of cP-containing 5′-tRNA halves.
(A) The targeted 5′-tRNA half’s regions are shown in black in the cloverleaf secondary structure of respective cytoplasmic tRNAs.
(B) In vitro synthesized HDV ribozyme and RRS-containing 5′-tRNA halves [5′-tRNALysCUU half (5′-LysCUU), 5′-tRNAHisGUG half (5′-HisGUG), and 5′-tRNAGlyGCC half (5′-GlyGCC)] were gel-purified and developed in denaturing PAGE.
(C) For trans-acting HDV ribozyme cleavage, the in vitro synthesized RNAs were incubated with HDV ribozyme for 10 min or 60 min. The bands of resultant cP-containing 5′-tRNA halves were observed after the cleavage reactions.
(D) The produced cP-containing 5′-tRNA halves were gel-purified and developed in denaturing PAGE.
(E) The 3′-terminal phosphate states of the produced 5′-tRNA halves were analyzed enzymatically. The RNAs were treated with CIP or T4 PNK (NT: nontreated samples used as negative controls) and subjected to 3′-AD ligation. The ligation efficiency was estimated by quantifying the AD-ligated RNAs using TaqMan RT-qPCR. The amounts from T4 PNK-treated RNA were set as 1, and relative amounts are indicated. Averages of three technical replicates with SD values are shown.