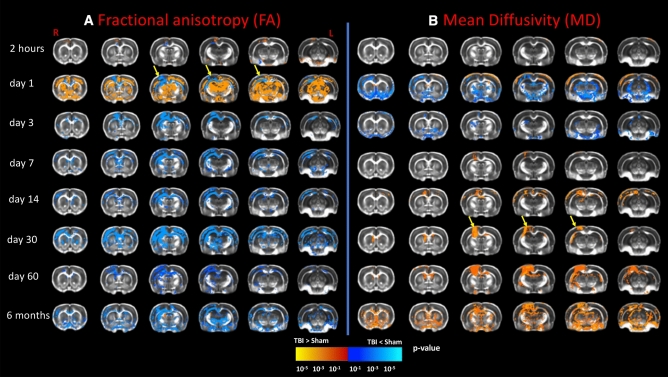
Figure 2.
The voxel-wise analysis results from the statistical differences (two-sample t-test) of the DTI measures between the TBI and sham groups as a function of time after injury to the right hemisphere. Results showed altered white matter and grey matter microstructure following TBI in (A) fractional anisotropy (FA) and (B) mean diffusivity (MD) images. (A) As compared to sham group, the longitudinal DTI analysis revealed reduced fractional anisotropy (FA) in the TBI group at different white matter tracts at from day1 and up to six months post-TBI, along with increased FA values in grey matter at two hours and day1 followed by widespread FA reduction in the grey matter up to six months post-TBI. In addition, longitudinal DTI reveals acute reduction in MD during the first three days post-TBI, followed by MD increase in white matter tracts beginning at day7 and persisting up the six months post-TBI. Moreover, MD values decline in grey matter at days 1 and 3, and then increased persistently until six months post-TBI. The yellow arrows point to the lesion area. All results were corrected for multiple comparisons using family wise error correction with p ≤ 0.05. Red-yellow represents increased DTI measures (FA and MD) in the TBI group as compared to sham group, while blue-green represents reduced DTI measures (FA and MD) in the TBI groups as compared to sham group.