Fig. 6. Schematic diagram deciphering the effect of GSK-3β on ferroptosis.
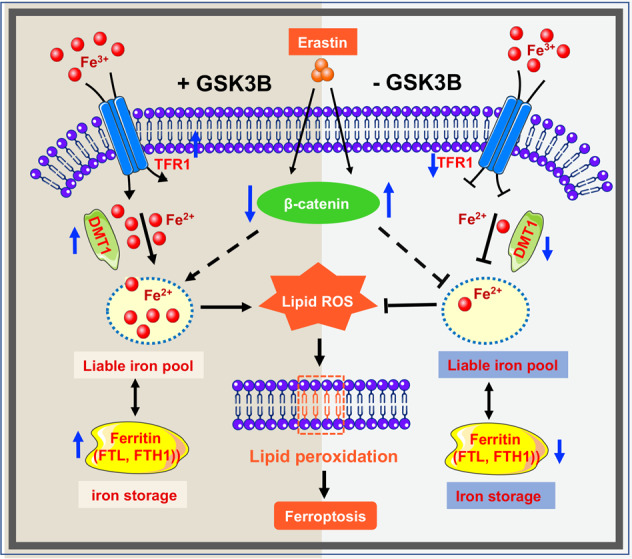
In the presence of GSK-3β (left half), erastin activates degradation of beta-catenin and enhances the transcription of iron uptake, transportation, and storage genes (DMT1, FTH1, and FTL), which leads to an increase in cellular iron concentration. Iron overload results in lipid peroxidation and eventually exerts ferroptosis. In the absence of GSK-3β (right half), erastin-induced ferroptosis is restrained through beta-catenin elevation, and dysregulation of iron metabolism-associated protein (DMT1, FTH1, and FTL), thus cellular labile iron pool is depleted. Decreased intracellular total iron levels and lipid peroxidation further limits erastin-induced ferroptosis.
