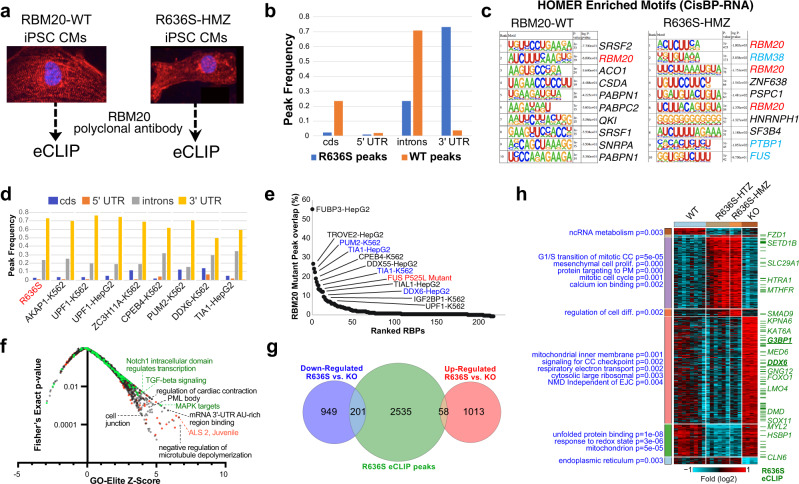
Fig. 3. RBM20 mutant protein preferentially binds to the 3′ UTR of novel transcripts.
a Illustration of the eCLIP strategy for wild-type and R636S HMZ iPSC-CMs. b Frequency of reproducible eCLIP peaks for WT and R636S HMZ iPSC-CMs within coding sequence (cds) exons, introns and UTR regions. c HOMER de novo motif enrichment logos and hypergeometric (default) enrichment p-values for the top-ranked RNA-binding protein recognition elements defined from the CisBP-RNA database. RBM20-associated motifs are highlighted in red and RNA-stabilization-associated factors in blue. d Frequency bar chart of reproducible peaks in R636S HMZ eCLIP and the most similar eCLIP profiles from ENCODE (K562 or HepG2 cells), based on correlation to their frequency profiles. e Overlap of R636S peaks in reproducible ENCODE eCLIP peaks, ranked by their percentage overlap. One previously described ALS eCLIP profile for the FUS-P525L mutation is included and highlighted in red, representing peaks only found in the FUS mutant compared to controls. Blue text indicates RBPs with statistically enriched RBM20 motifs based on HOMER (Supplementary Fig. 4b). f Gene-set enrichment with GO-Elite (Fisher Exact test p < 0.05, raw) of genes associated with FUS-P525L and R636S overlapping peaks, for disease-associated gene-sets (red, DisGeNET), aggregate pathways (green, ToppFun), and Gene Ontology (black). g Overlap of genes up- or down-regulated by RNA-Seq in R636S iPSC-CMs (HTZ+HMZ) versus RBM20 deletion and R636S eCLIP peaks (eBayes two-sided t-test p < 0.05, FDR corrected). h Heatmap of all statistically ranked and organized (MarkerFinder algorithm) RBM20 R636S or deletion genes in iPSC-CMs by RNA-Seq. Statistically enriched gene-sets (GeneOntology + PathwayCommons) are indicated in blue with their associated Fisher’s Exact test p-value (unadjusted) and R636S eCLIP peaks indicated by a green dash (selected genes shown). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.