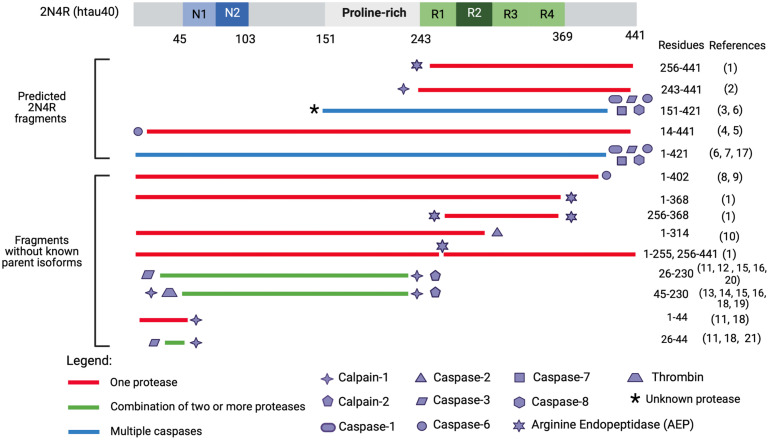
FIGURE 4.
Tau fragments found in in vitro and in vivo models with pathogenic functions and processing proteases. This figure illustrates a select group of tau proteolytic fragments which have been shown to have to drive neurotoxicity in either in vitro or in vivo models (correlated with Tables 1, 2) and have a known responsible protease. Precipitating proteases are represented by shape symbols and tau fragments are colored coded based on whether they are cleaved by one or multiple proteases. The top fragments are hypothesized to derive from 2N4R isoform as they extend past aa 410, which is the termination point of the second largest tau isoform, 2N3R. Several fragments from Gu et al. (2020) including tau 51–391, tau 51–421, tau 51–441, tau 151–391, tau 231–391, tau 231–421, and tau 231–441 are not included as they were engineered through recombinant plasmid techniques and have not been identified endogenously. Tau 187–441 and tau 1–391 are excluded as it is unclear which proteases cleaves at G186-E187. Tau 1–156 is excluded as it is unclear if thrombin, which cleaves at R155-G156 (Arai et al., 2005) also cleaves at G156-A157. The * symbol indicates that it is unknown what protease cleaves at the N-terminus of tau 151-421. Tau proteolytic fragments have not been studied to precipitate in up-regulated concentrations from 3R- or 4R-isoforms, and it is unclear whether 3R- or 4R-isoforms more toxic fragments. Reference numbers in parentheses refer to cited articles as follows: (1) Zhang et al. (2014); (2) Matsumoto et al. (2015); (3) Ozcelik et al. (2016); (4) Horowitz et al. (2004); (5) Horowitz et al. (2004); (6) Gamblin et al. (2003); (7) Quintanilla et al. (2009); (8) Foveau et al. (2016); (9) Guo et al. (2004); (10) Zhao et al. (2016); (11) Amadoro et al. (2006); (12) Amadoro et al. (2012); (13) Lang et al. (2014); (14) Afreen et al. (2017); (15) Park and Ferreira (2005); (16) Garg et al. (2010); (17) Matthews-Roberson et al. (2008); (18) Yang and Ksiezak-Reding (1995); (19) Arai et al. (2005); (20) Corsetti et al. (2008); and (21) Florenzano et al. (2017).