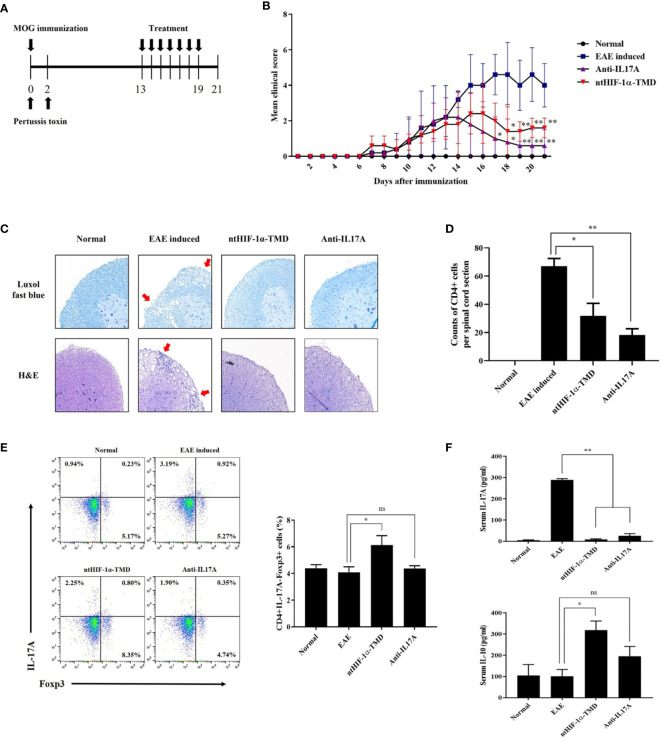
Figure 4.
Therapeutic potential of ntHIF-1α-TMD in EAE disease models. (A) The treatment scheme of EAE-induced mice with phosphate-buffered saline (EAE induced), ntHIF-1α-TMD (100 μg/mouse), or anti-IL17A (40 μg/mouse) is represented. (B) A clinical score was measured until 21 days after EAE induction. (C) EAE-induced mice (w/or w/o treatment) were sacrificed 16 days after EAE induction. The spinal cords were harvested, and the histological analysis was performed by Luxol Fast Blue (C, upper panel) and H&E (C, lower panel) staining. (D) CD4+ T cells infiltrated into the spinal cord in (C) were counted, and the graph is represented as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 4). (E) CD4+ T cells in the lymph nodes harvested from the mice at day 16 were analyzed for the expression of IL-17A or Fopx3 by flow cytometry. (F) The level of IL-17A or IL-10 in the serum of mice at day 16 was measured by ELISA. The graphs are represented as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3). The experiments in EAE disease model were independently performed three times. The group differences were analyzed by Student’s t-test as a statistical analysis. ns, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.