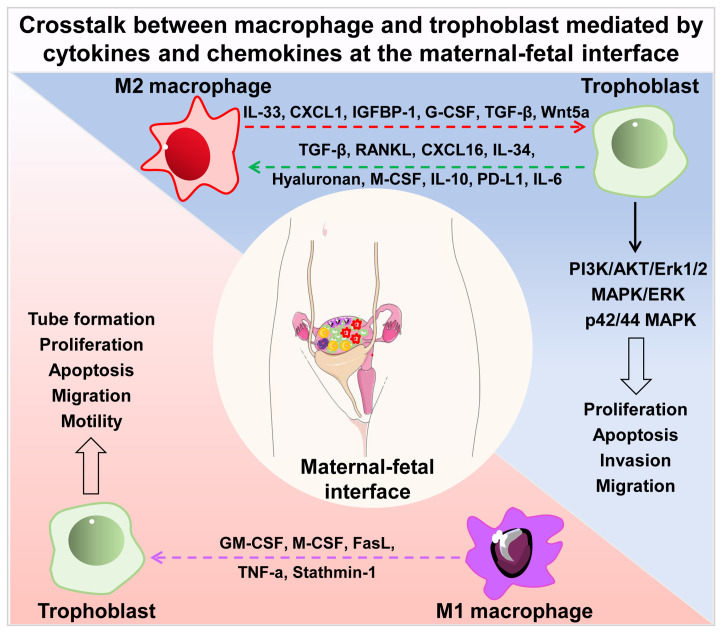
Figure 1.
Crosstalk between macrophage and trophoblast mediated by cytokines and chemokines at the maternal-fetal interface. Cytokines and chemokines secreted by M2 macrophages (IL-33, CXCL1, IGFBP1, G-CSF, TGF-β, Wnt5a) regulate the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and migration of trophoblast via PI3K/AKT/Erk1/2, MAPK/ERK and p42/44 MAPK signal pathways. Trophoblast- derived secretory factors (TGF-β, RANKL, CXCL16, IL-34, hyaluronan, M-CSF, IL-10, PD-L1, IL-6) drive M2 macrophage polarization in turn. Soluble molecules secreted by M1 macrophages (GM-CSF, M-CSF, FasL, TNF-a, Stathmin-1) influence the tube formation, proliferation, apoptosis, migration and motility of trophoblast. IL, interleukin; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; IGFBP1, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1; G-CSF, granulocyte colony stimulating factor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; RANKL, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand; M-CSF, macrophage colony stimulating factor; PD-L1, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; FasL, factor associated suicide ligand; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α.