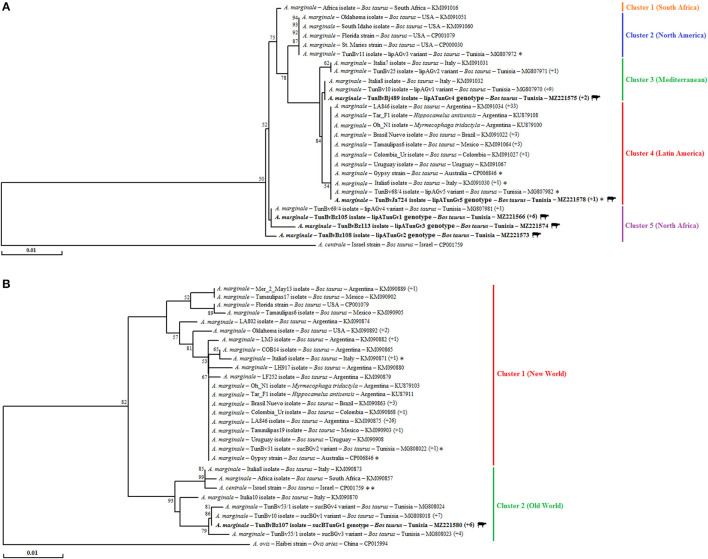
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree showing all Anaplasma marginale genetic variants based on multiple alignment of lipA (A) and sucB (B) partial nucleotide sequences (501 and 681 bp, respectively) using the “neighbor-joining” method. The numbers related to the nodes represent robustness rates over 1,000 iterations supporting the nodes (only rates >50% are shown). The host, strain or isolate, country of origin, and GenBank accession number are indicated. The sequences of A. marginale newly obtained in the present study are in bold and marked with a bovine picture. Sequences that are not classified into their appropriate geographic regions represented by clusters are indicated with an asterisk. The numbers that are in parentheses at the end of some sequences represent isolates or strains that are represented by an identical sequence from the isolate or strain present in the tree.