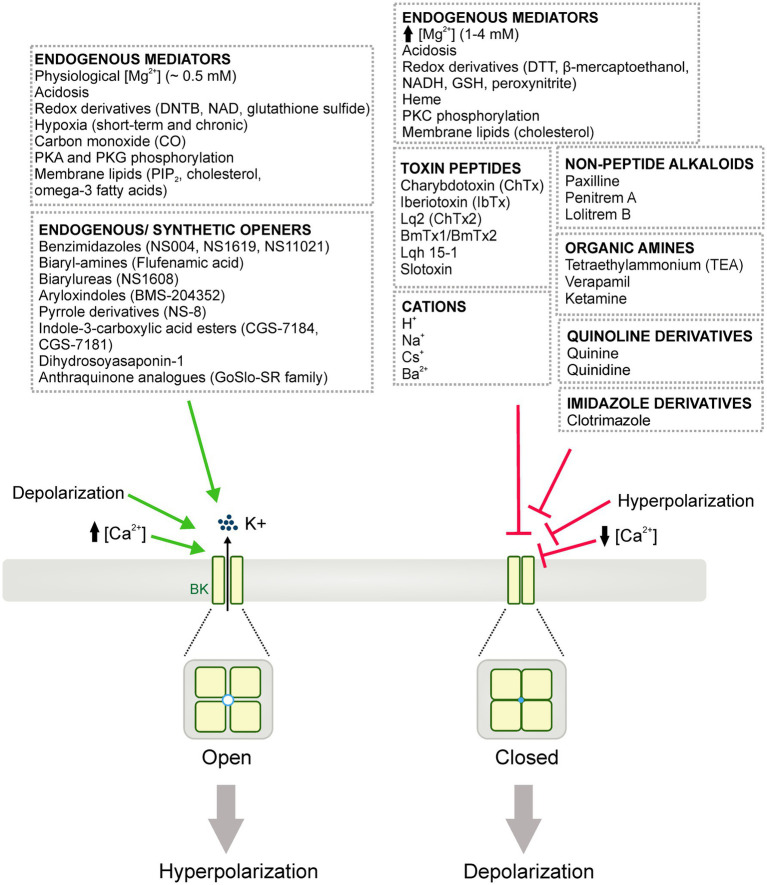
Figure 3.
Diagrammatic summary of the pharmacology of BK channels. BK channels can be activated (i.e., opened) or blocked (i.e., closed or inhibited) leading to cell membrane hyperpolarization and depolarization, respectively. Diverse endogenous mediators, redox derivatives and, signaling proteins are able to either potentiate or inhibit BK channel activity. Numerous BK channel inhibitors/blockers have been also reported, including: toxin peptides from scorpion venoms, non-peptide alkaloids, organic amines, quinolone and imidazole derivatives. Additionally, an extensive list of cations including H+, Na2+, Cs+ and Ba2+ are shown to influence BK channel activity. Similarly, endogenous and synthetic openers have been widely studied as experimental tools and potential therapeutic approaches for different vascular or neurological disorders involving BK channels.