Figure 3.
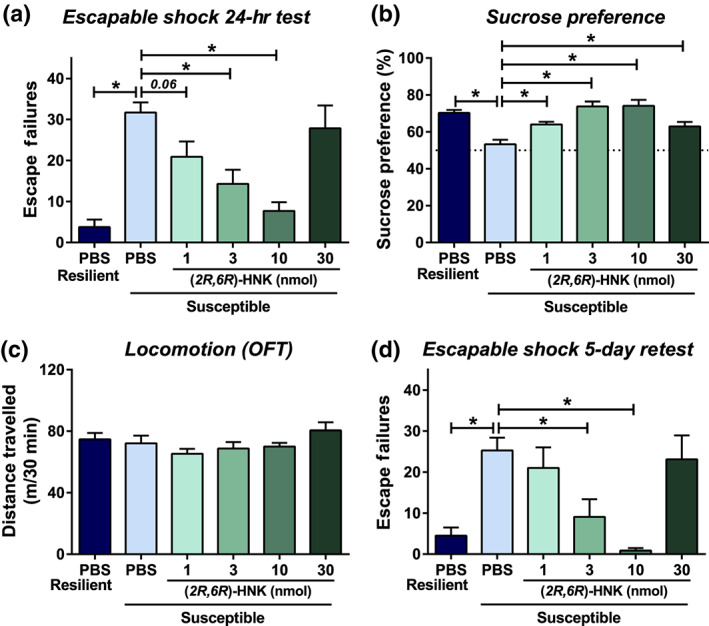
Intracerebroventricular administration of (2R,6R)‐hydroxynorketamine exerts rapid and long‐lasting antidepressant‐relevant behavioural actions in mice. Following inescapable shock and screening for escape deficits, mice were given intracerebroventricular infusions of vehicle or different doses of (2R,6R)‐hydroxynorketamine (HNK). For a timeline, see Figure 2c. (a) Twenty‐four hours following treatment, mice were tested for helpless (escape deficits) behaviour, where (2R,6R)‐HNK dose dependently reduced escape deficits. (b) (2R,6R)‐HNK reversed inescapable shock‐induced sucrose preference deficits in susceptible mice at all doses. (c) No differences in locomotor activity of mice were observed in any treatment group. (d) To assess for long‐term antidepressant‐relevant actions, mice were retested for shock‐induced escape deficits 5 days post‐injection. (2R,6R)‐HNK administration manifested long‐lasting antidepressant‐relevant actions in this paradigm. Data are the mean ± SEM. *P < .05, significantly different as indicated. See Tables 2 and S1 for statistical analyses and precise group sizes
