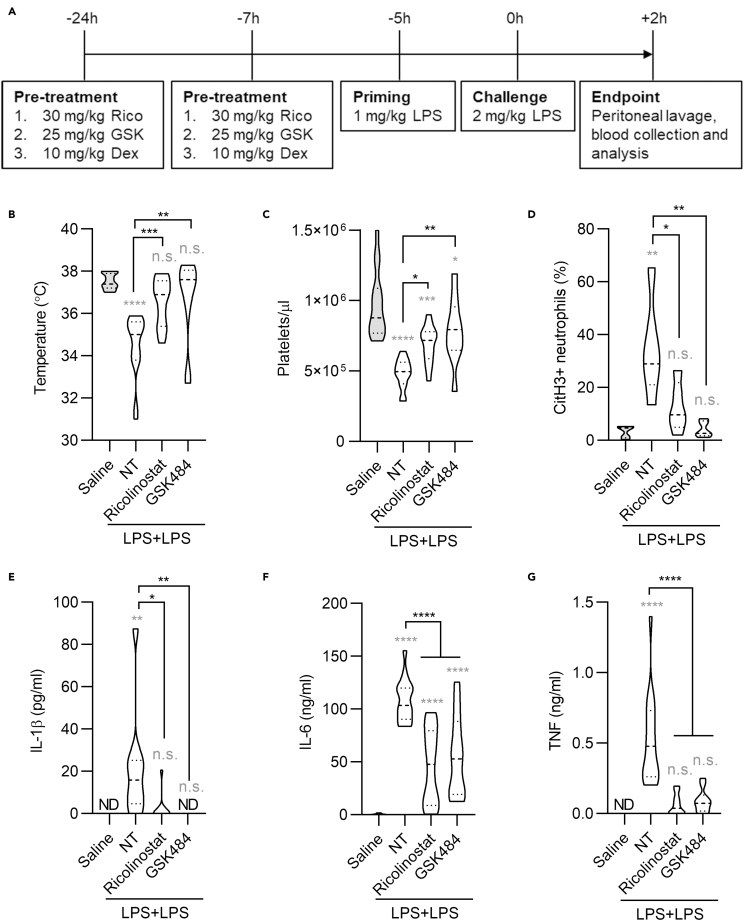
Figure 4.
Class I/IIb HDAC inhibition protects against systemic inflammation
(A) Time line of drug treatment and LPS priming and challenge. Mice were intraperitoneally injected, or not, with two doses of ricolinostat or GSK484 and were then intraperitoneally administered with two doses of LPS (-5 h, 1 mg/kg and 0 h, 2 mg/kg) to induce lethal sepsis. Peritoneal lavage and blood were collected 2 h after the LPS challenge.
(B) Body temperature was measured 2 h post challenge.
(C) Concentration of platelets in the blood was measured by cytofluorimetry.
(D) NETosis was measured as neutrophils (Ly6G+/CD11b+) positive for citrullinated histone H3 staining in the peritoneal lavage.
(E–G) Serum cytokines were measured by ELISA. The NT group represents mice that were challenged with LPS and did not receive any drug. Statistics were calculated using one-way ANOVA (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant). n = 15 for each group except the GSK484-treated group (n = 10). Gray stars represent comparison of all experimental groups with the saline-treated healthy control. Black stars represent comparison of drug-treated groups with LPS-stimulated mice without drug treatment. Violin plots represent median (dashed line) with quartiles (dotted line). See also Figure S4.