Figure 4.
Role of PFDNs in mammals
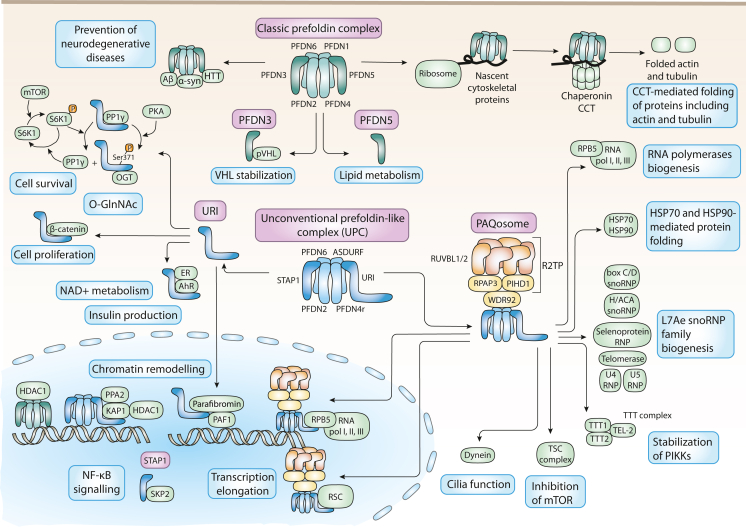
In mammals, the classic PFDN complex is formed by PFDNs 1 to 6. As in yeasts, it binds to nascent actin and tubulin cytoskeletal proteins to deliver them to the chaperonin CCT to promote their folding. The chaperone activity of the complex has been also associated to proteins involved in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Aβ oligomers, α-synuclein, or huntingtin (HTT). Apart from these functions within the complex, PFDN 3 is also involved in the stabilization of pVHL; and PFDN 5 has been associated with lipid metabolism. Mammals also present the unconventional or URI PFDN-like complex (UPC). It is involved in chromatin remodelling functions, for example by binding KAP1 and PPA2 together to allow the regulation of the histone deacetylase HDAC1. UPC also binds to the R2TP module to form a complex termed PAQosome that has been involved in the assembly of other protein complexes, such as the RNA polymerases, L7Ae snoRNP family of ribonucleoproteins, or PIKKs through the interaction with the TTT complex. The PAQosome is also involved in protein folding since it interacts with the chaperones HSP70 and 90, and is related to other cellular processes such as inhibition of mTOR through interaction with the TSC complex or the cilia function though its interaction with dynein. In the nucleus, the PAQosome promotes transcription elongation by its interaction with the polymerases and with chromatin remodeling complexes such as RSC. The UPC component URI has also shown other functions besides its contribution to the UPC. URI affects cell survival thanks to its relationship with PP1γ, and also cell proliferation by binding to β-catenin and thus preventing its translocation to the nucleus to promote cell proliferation and by affecting O-Glucosyl N-Acetylation of proteins like c-Myc by its PKA-dependent interaction with OGT. Furthermore, loss of URI has been associated with an increase in DNA damage, at least in part by binding to AhR and ER receptors and thus affecting NAD+ metabolism. URI binding to these receptors also affects insulin production in β-cells in the pancreas. URI also affects chromatin remodeling in the nucleus by interacting with parafibromin and PAF1. The other alfa protein forming the UPC, STAP1, is also involved in other functions beyond the UPC, for example in NF-κB signaling.