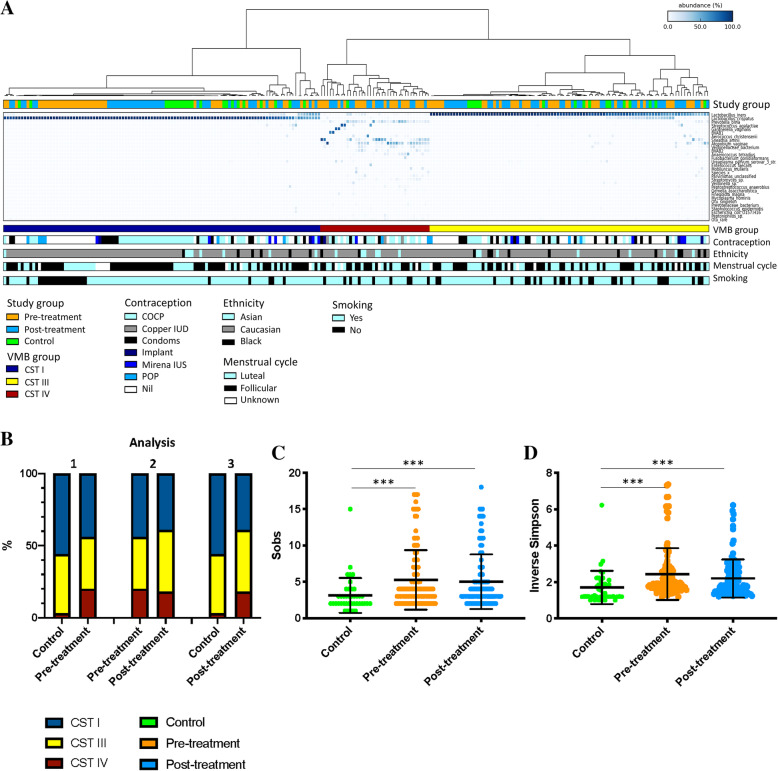
Fig. 2.
Heatmap showing the vaginal microbiota composition in 103 women before (orange) and after (blue) excisional treatment and in 39 healthy, untreated controls (green) (A) and changes in richness (C) and diversity (D) indices associated with disease status. A Three of the previously described community state types (CSTs) were identified in our cohort. B CST IV was significantly more prevalent in the treatment cohort both before and after treatment compared to 39 untreated controls (p = 0.0081 and 0.0142, respectively, chi-squared test). There was no significant change in the vaginal microbiome composition before and after treatment. C Richness was significantly greater in women planned for excision both before (p = 0.0003, unpaired t test) and after (p = 0.0005, unpaired t test) treatment when compared to healthy untreated controls. D Diversity was also increased in women planned for treatment before (p < 0.0001, unpaired t test) and after (p = 0.0005 unpaired t test) treatment compared to controls. Richness or diversity was no different before and after treatment. CST, community state type; Sobs, species observed; VMB, vaginal microbiota. Dots depict the individual samples; error bars denote mean ± standard deviation, ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05)