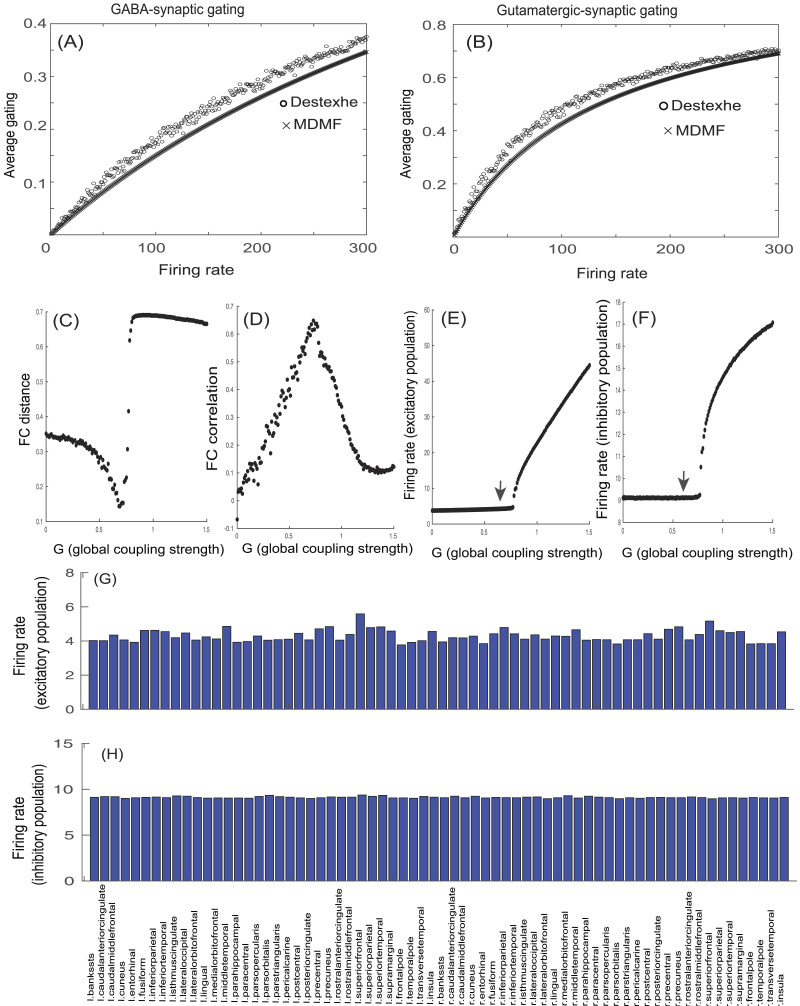
Figure 2. .
Comparison of MDMF model prediction of synaptic gating variables at steady state and the gating kinetics model proposed by Destexhe et al. (1994b). Model-generated average (A) GABA- or (B) NMDA-synaptic gating as a function of population mean firing rate (dotted lines) closely approximates the model proposed by Destexhe et al. (1994b) (lines with empty circles). (C) FC distance is examined as a function of G; each point represents FC distance for each G value. (D) FC correlation is examined as a function of G; each point represents FC correlation for each G value. For G = 0.69, FC distance is found to be minimum, whereas FC correlation is found to be maximum. (E) Average firing rate of excitatory population as a function of G; each point represents average firing rate of excitatory population for a specific G value. For G = 0.69, average firing rate of excitatory population is ∼4 Hz (represented by black arrow). (F) Mean firing rate of inhibitory population as a function of G; each point represents mean firing rate of inhibitory population for a specific G value. For G = 0.69, average firing rate of inhibitory population is ∼9 Hz (denoted by black arrow). (G) Firing rate of excitatory populations of all 68 brain areas (Desikan-Killiany atlas) is shown for G = 0.69. (H) Firing rate of inhibitory populations of all 68 cortical areas is shown for G = 0.69.