Figure 5. The VP40 ring generated using 3′ UTR-inspired nucleic acids aligns with known ring structures.
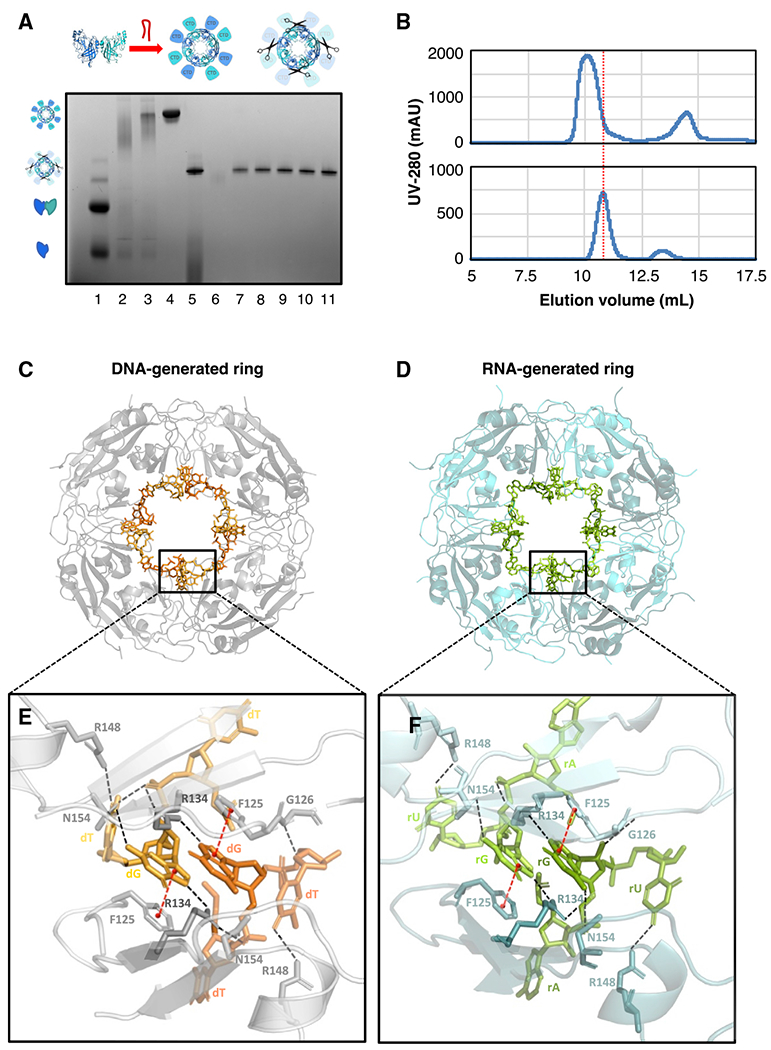
(A) VP40 including a TEV protease recognition site was expressed, after which the purified VP40 monomer/dimer was incubated with RNA or DNA to generate the ring, and finally TEV protease was applied to delete the C-terminal domains (CTDs). A blue native protein gel verifies the creation of the CTD-deleted ring using the 3′ UTR-inspired HSP DNA oligo (Table S2). The VP40 monomer/dimer (lane 1), the VP40 endogenous ring (lane 2), the ring generated from the monomer/dimer by the DNA incubation (lane 3), the DNA-generated ring after SEC purification (lane 4), the CTD-deleted ring after the TEV protease digestion (lane 5), and the fractions after a final SEC purification (lanes 6–11) are shown.
(B) Two SEC traces from the above protocol. Top: after the incubation of the VP40 monomer/dimer with the HSP DNA, the full-length VP40 ring elutes at 10.1 mL. Bottom: after the subsequent TEV protease digestion, the CTD-deleted VP40 ring elutes at 10.8 mL.
(C) Our crystal structure at 1.78-Å resolution of the VP40 octameric ring generated using the HSP DNA oligo (PDB: 7K5D). Eight symmetry-related DNA fragments are seen bound to the ring.
(D) Our crystal structure at 1.38-Å resolution of the VP40 octameric ring generated using the HSP RNA oligo (PDB: 7K5L). Eight symmetry-related RNA fragments are seen bound to the ring. The structures in (C) and (D) align closely, with protein backbone RMSD of 0.10 Å.
(E) A detail from (C) of two DNA fragments bound to the ring. The two DNA fragments are symmetrical to each other and share a binding cleft between two VP40 molecules that are also symmetrical to each other. Each DNA fragment has been built as 5′-TGT-3′. Hydrogen bonds are indicated with dashed black lines, pi stacking with red lines. The central guanine nucleotide is key to the DNA-protein interface, interacting with both of the adjacent VP40 molecules: its phosphate interfaces with R134 and N154, while its base interfaces with F125 and with R134 and N154 again. The third nucleotide (thymine) interfaces with R148, G126, and N154 again. See also Figure S5A.
(F) A detail from (D) of two RNA fragments bound to the ring. Each RNA fragment has been built as 5′-AGU-3′. The nucleic acid-protein interface closely resembles that seen in (E), particularly with regard to the central guanine nucleotide. See also Figure S5B.
