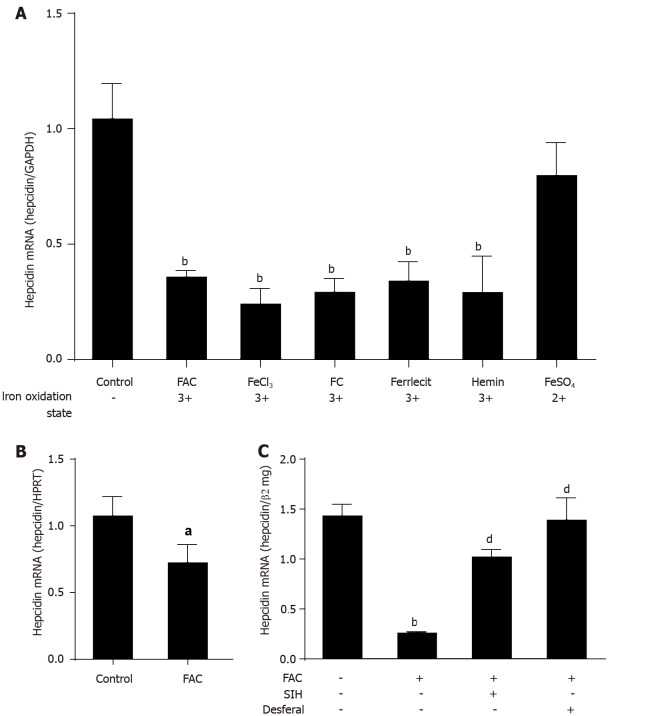
Figure 1.
Efficient suppression of hepcidin by higher iron levels. A: Huh7 cells were treated with 50 μmol/L of FAC, FeCl3, FC, ferrlecit, hemin or FeSO4 for 24 h; B: Murine primary hepatocytes were treated with FAC (50 μmol/L) for 24 h; C: Huh7 cells were treated with FAC (50 μmol/L) in the presence or absence of SIH (100 μmol/L) or Desferal (50 μmol/L) for 24 h. Total RNA was extracted from Huh7 cells or murine primary hepatocytes. Hepcidin mRNA levels were determined by quantitative real-time PCR, normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase or hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase or β2mg. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001 vs control; dP < 0.001 vs FAC group. FAC: Ferric ammonium citrate; FeCl3: Ferric chloride; FC; Ferric citrate; FeSO4: Ferrous sulfate; SIH: Salicylaldehyde isonicotinoyl hydrazine; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; β2mg, β2-microglobulin; HPRT: Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase.