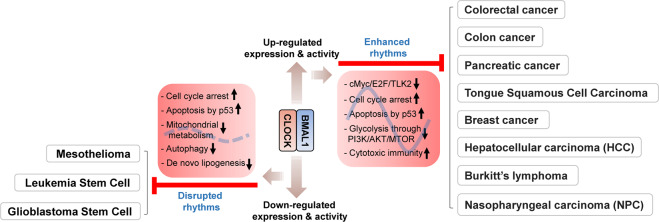
Fig. 4. Divergent roles of circadian clock components in cancer.
Enhanced levels or activity of circadian clock components (e.g., CLOCK/BMAL1) inhibit tumor proliferation and growth by promoting the degradation of oncoproteins (e.g., cMYC, E2F, and TLK2), cell cycle arrest, apoptotic cell death, metabolic defects, and cytotoxic immunity in multiple cancers, as indicated. On the other hand, the core clock components may also exert tumor-suppressive functions in some cancer cell types (e.g., mesothelioma, leukemia stem cells, glioblastoma stem cells) by inhibiting tumor progression upon downregulation. E2F early 2 factor, TLK2 tousled like kinase 2.