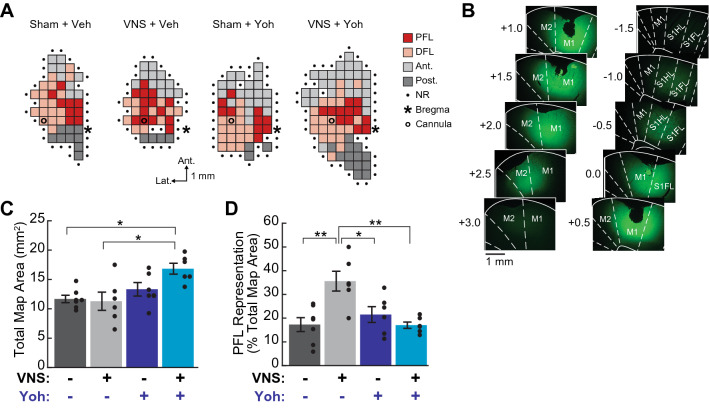
Figure 2.
Cortical infusion of selective α2-AR antagonists blocked VNS-induced motor map reorganization. (A) Example cortical motor maps from subjects in each treatment group; representative maps are from subjects in each group that exhibited the median total map area and proximal forelimb (PFL) representation for that group. DFL: distal forelimb; Ant.: anterior body representation (vibrissa, head, or neck); Post.: posterior body representation (trunk, hindlimb, or tail); NR: non-responsive. (B) Cannula infusion of 1 μL sodium fluorescein dye was used to estimate drug diffusion within the cortex. (C) Total motor map area was significantly larger in VNS treated rats that received yohimbine (yoh) infusion compared to other groups. (D) To control for variation in total map size across subjects, subregion areas were normalized to total map area for each subject. VNS paired with lever training significantly enlarged the normalized PFL representation in vehicle-infused rats. In yohimbine-infused rats, VNS-driven PFL expansion was blocked. In (C), (D), filled circles indicate data for individual rats; error bars denote SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, Tukey post hoc comparison.