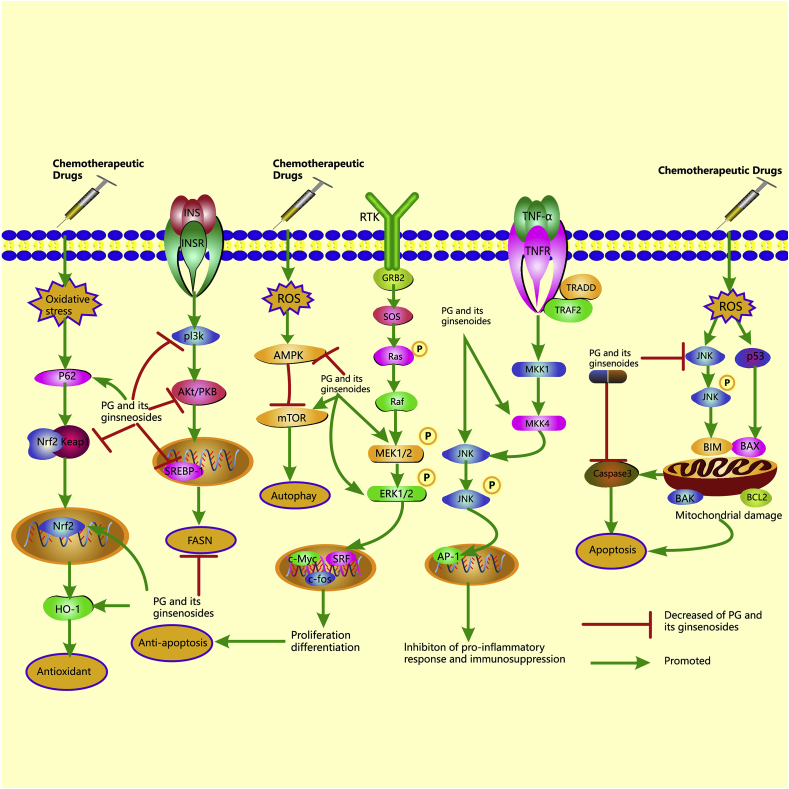
Fig. 2.
The molecular protective mechanisms of PG and its ginsenosides against chemotherapy-induced side effects. PG or its ginsenosides can regulate Nrf2/HO-1, P62/keap1/Nrf2, JNK/P53/caspase3, MEK/ERK, AMPK/mTOR, MKK4/JNK, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Nrf2/HO-1 and P62/keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathways are classic antioxidant pathways. PG or its ginsenosides exert antioxidant effects by up-regulating P62, Nrf2, and HO-1 expressions and down-regulating keap1 expression. JNK/P53/caspase3 and MEK/ERK signaling pathways are related to cell apoptosis. PG or its ginsenosides show anti-apoptosis effects by inhibiting the activation of JNK, P53, and caspase3 and activating the expressions of MEK and EKR. AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the genesis and progression of autophagy. PG or its ginsenosides regulate AMPK/mTOR pathways by increasing mTOR expressions and suppressing AMPK expressions. MKK4/JNK is an essential pathway by which PG and its ginsenosides alleviate chemotherapy-induced immunosuppression. PG and its ginsenosides regulate MKK4/JNK pathways by promoting MKK4 and JNK expressions. The regulation of fatty acid synthase (FASN) is associated with immunomodulatory effects. PG or its ginsenosides regulate FASN by inhibiting the activation of PI3K, AKT, and SREBP-1.