FIG 5.
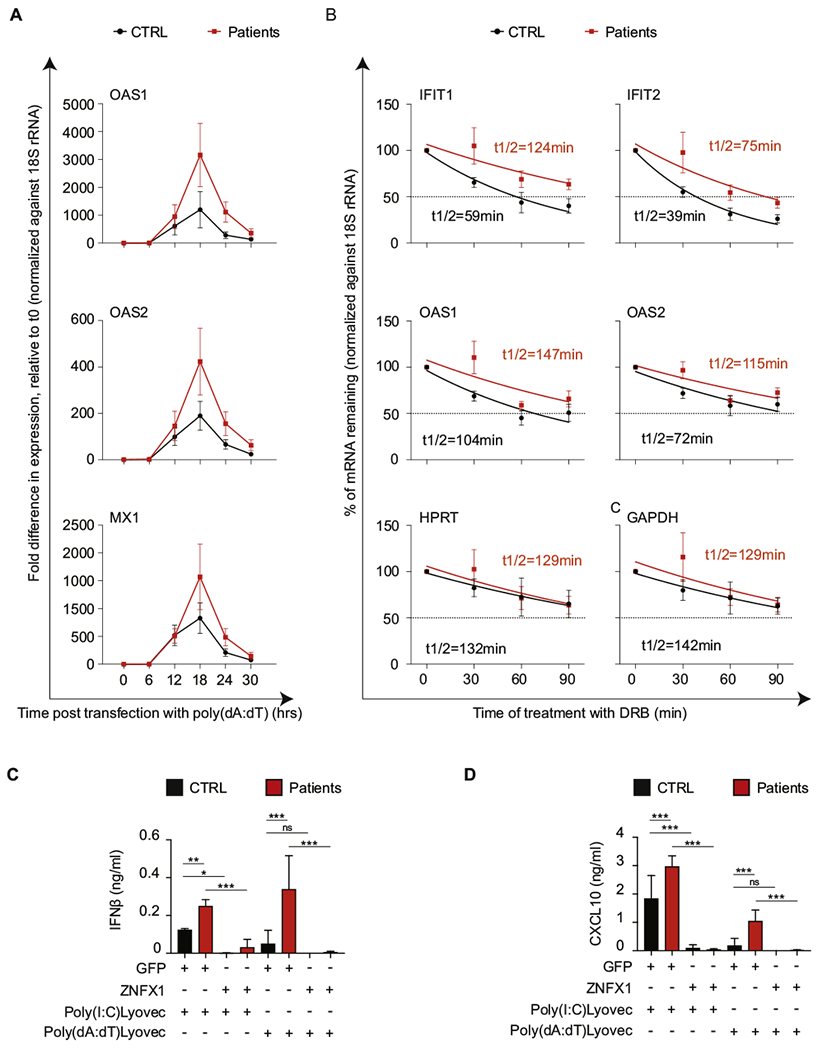
Increased ISG expression in response to transfected poly(dA:dT) in biallelic defects in ZNFX1 is associated with increased mRNA stability. A, The mRNA expression levels of OAS1, OAS2, and MX1 (representative ISGs) by skin fibroblasts from P1.2, P2.1, P3.2, and P5.2 (red squares) and 4 healthy controls (CTRLs) (black circles) at baseline (zero hours) and at different time points (6, 12, 18, 24. and 30 hours) after stimulation with transfection reagent–complexed poly(dA:dT). B, Mean values of mRNA stability of representative ISG mRNAs in fibroblasts from 4 healthy controls and 4 patients (P1.2, P2.1, P3.2, and P5.2). Gene transcription was inhibited by the addition of 5,6-dichlorobenzimidazole 1-β-D-ribofuranoside (DRB) 18 hours after transfection with LyoVec-poly(dA:dT).qPCR was performed at the indicated time points after the addition of DRB. The amount of mRNA at each time point was normalized against ribosomal 18S RNA and represented relative to the amount at the time of DRB addition (time zero). The half-life (t1/2) of each mRNA (red for P1.2 and black for CTRL) was calculated by using nonlinear regression analysis. A representative result of 3 independent experiments is shown. Concentrations of IFN-β (C) and CXCL10 (D) in the supernatant of dermal fibroblasts from 3 healthy controls (CTRL [black bars]) and 3 patients (P1.2, P3.2, P5.2 [red bars]) following 18 hours of stimulation with poly(I:C)LyoVec or poly(dA:dT)LyoVec. Fibroblasts were transfected with plasmids expressing ZNFX1 or green fluorescent protein. Shown is the mean of 3 repeats for each of the 3 samples(n = 9), with error bars showing the SD. P values were calculated by using ordinary 1-way ANOVA as follows: ns = 0.12; *P = .033l; **P = .002; and ***P < .001.
