Figure 3.
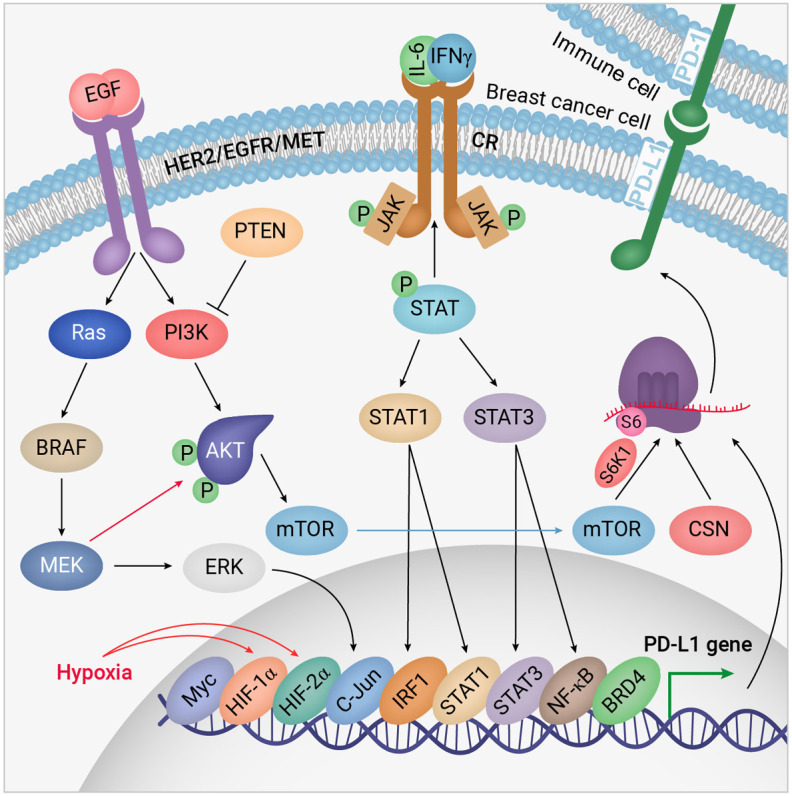
Collaborations of Akt, MAPK, and JAK/STAT pathways in suppressing the anti-cancer immune system. Under hypoxic conditions provided by Akt signalling, PD-L1 is expressed by breast cancer cells to inhibit T-cells. Three main signalling pathways are involved. RTKs triggers PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways, whereas cytokine receptors (CR) are activated by cytokines released into the TME. JAK/STAT signalling is then activated to recruit STAT1/3 and other transcription factors on some specific gene promoters including the PD-L1 promoter. Simultaneously, proliferation and metastasis are activated and anti-cancer immunity inactivated. S6 and CSN are ribosomal protein S6 and components of the eukaryotic translation factors 3 (eIF-3) complex, respectively, involved in protein synthesis. “Redesigned from Pharmacological Research, Volume 156, Jabbarzadeh Kaboli et al., Akt-targeted therapy as a promising strategy to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer-A comprehensive review from chemotherapy to immunotherapy, 104806, Copyright (June 2020), with permission from Elsevier”.
