Figure 3.
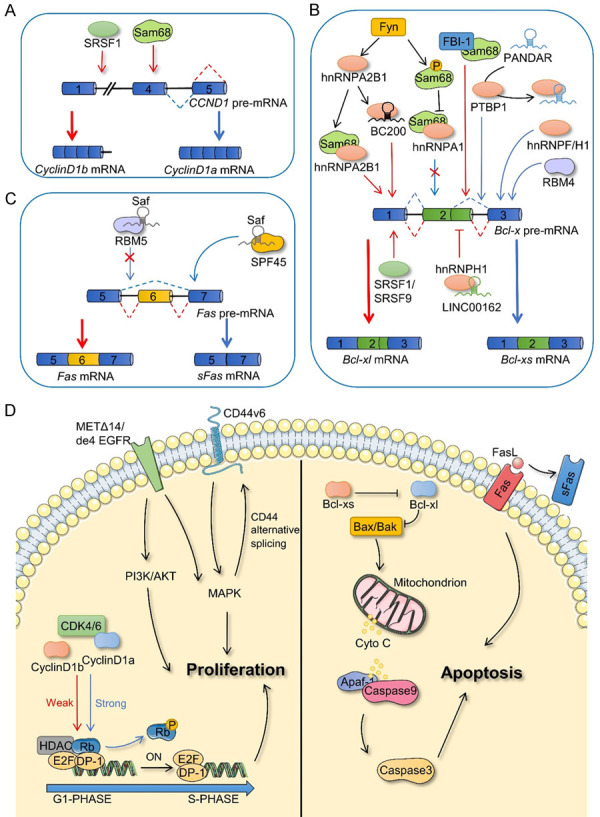
Alternative splicing in cell proliferation and apoptosis. A. Splicing factors affect the alternative splicing process of CCND1. B. The pathways involved in the alternative splicing of Bcl-x to form Bcl-xl and Bcl-xs isoforms. C. Fas and sFas are alternative splicing products of Fas. D. CCND1 splicing products (Cyclin D1b and Cyclin D1a), CD44 splicing products (CD44v6), and receptor tyrosine kinase families (METΔ14 and de4 EGFR) affect cell proliferation (left). Splicing products of Fas and Bcl-x play a functional role in apoptosis (right). SRSF1, serine and arginine rich splicing factor 1; Fyn, Src family tyrosine kinase; FBI-1, factor binding IST protein 1; RBM5, RNA-binding motif 5; RBM4, RNA-binding motif 4; SPF45, RNA binding motif protein 17; PTBP1, epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1; hnRNPA1, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1; hnRNPA2B1, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1; hnRNPH1, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H1; hnRNPF, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein F; SRSF9, serine and arginine rich splicing factor 9; METΔ14, MET which lacks exon 4; de4 EGFR, EGFR which has exon 4 excluded; CDK4/6, cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6; HDAC, histone deacetylase; P, phosphorylation; Bcl-x, B-cell leukemia x; Bcl-xs, Bcl-x short isoform; Bcl-xl, Bcl-x long isoform; BAX, BCL2-associated X; BAK, BCL2 Antagonist/Killer 1; Apaf-1, Apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1; Cyto C, Cytochrome C; Fas, Fas cell surface death receptor; sFas, soluble Fas; FasL, Fas ligand.
