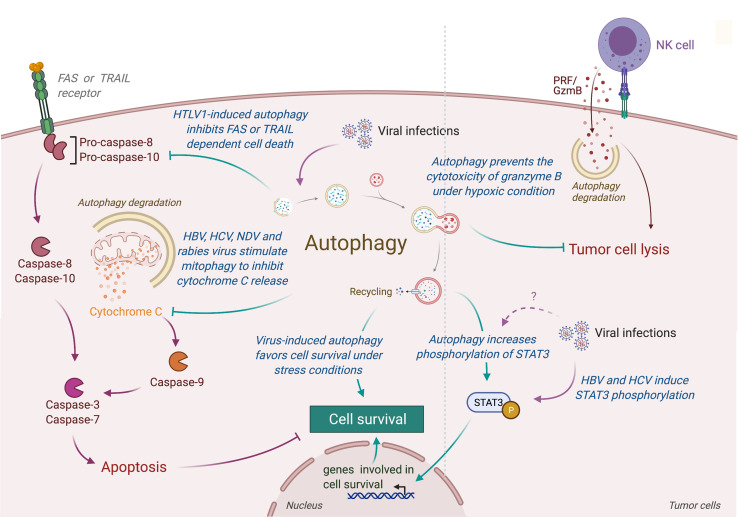
Figure 4.
Role of virus-induced autophagy in tumor cell survival. Viral infections can induce autophagy in tumor cells, leading to a protection of tumor cells from stress-induced or immune cells-induced cell death. In one hand, autophagy protects tumor infected cells from stress conditions (e.g., starvation or hypoxia) by limiting the accumulation of damaged organelles or by increasing the expression of genes involved in cell survival (e.g., via the phosphorylation of SATA3). In another hand, virus-induced autophagy limits the induction of apoptosis, protecting tumor cells from death receptor- or mitochondria-mediated cell death. Autophagy also takes part in the resistance of infected tumor cells from immune cell lysis by targeting and neutralizing granzyme B activity. HTLV-1, Human T cell Leukemia/lymphoma Virus type 1; HBV, Hepatitis B Virus; HCV, Hepatitis C Virus; NDV, Newcastle Disease Virus; PRF/GzmB, Perforin/Granzyme B.