Figure. Association of Genetically Predicted Modifiable Risk Factors With Advanced Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) and its Subtypes.
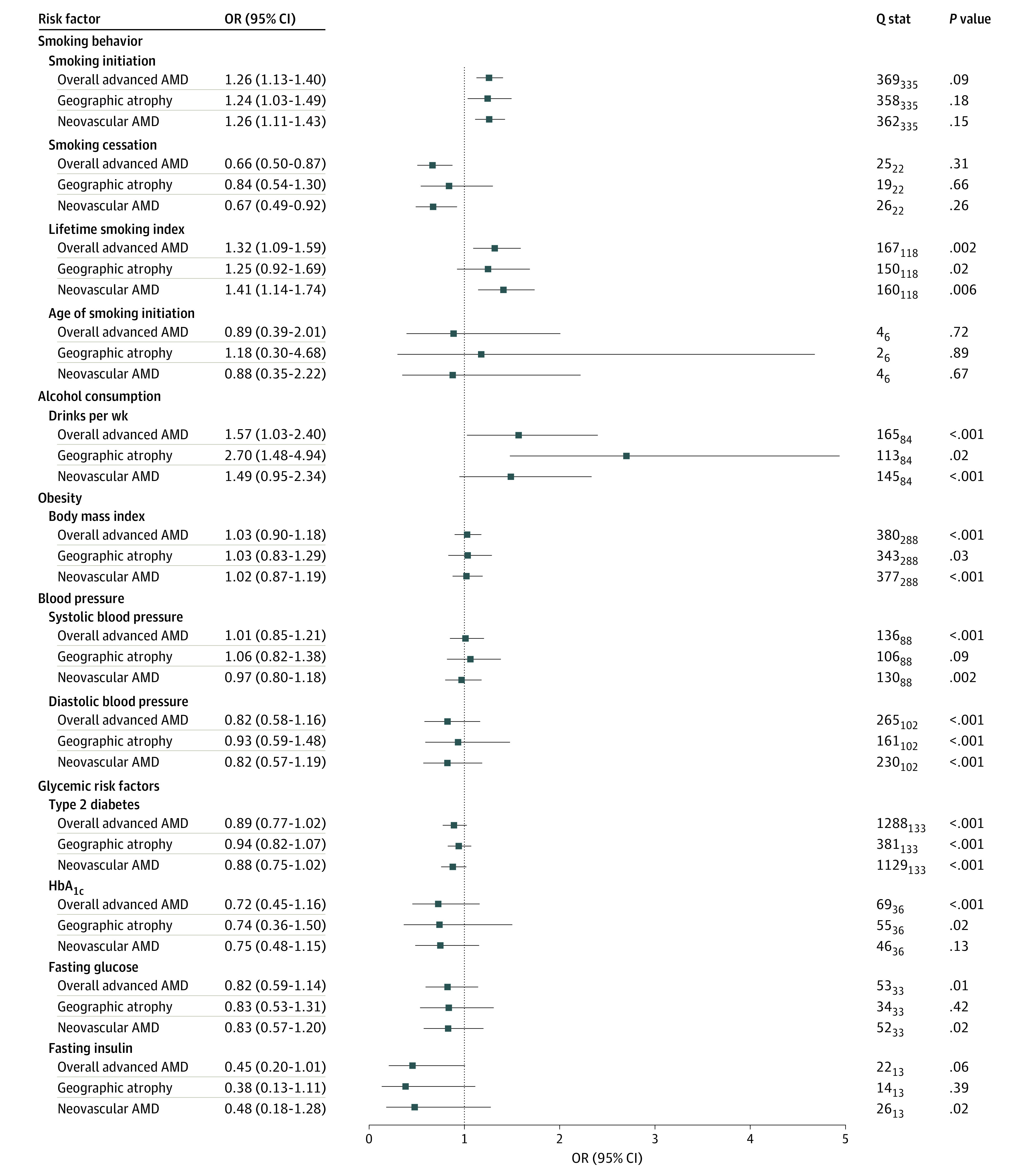
Odds ratios under the inverse-variance weighted mendelian randomization method are shown for a 1-SD increase in the logodds of ever having smoked regularly, 1-SD increase in the logodds of smoking cessation (former vs current smoking), 1-SD increase in the lifetime smoking index, 1-SD increase of the age at which an individual started smoking regularly, 1-SD increase of log-transformed alcoholic drinks per week, 1-SD increase in body mass index (calculated as 4.8 kg/m2); 10-mm Hg increase in systolic and diastolic pressure; 1-SD increase in the logodds of having type 2 diabetes; 1% increase in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c); 18.02-mg/dL (to convert to mmol/L, multiply by 0.0555) increase in fasting glucose; and 1 log-transformed (pmol/L) increase in fasting insulin.
