Figure 4.
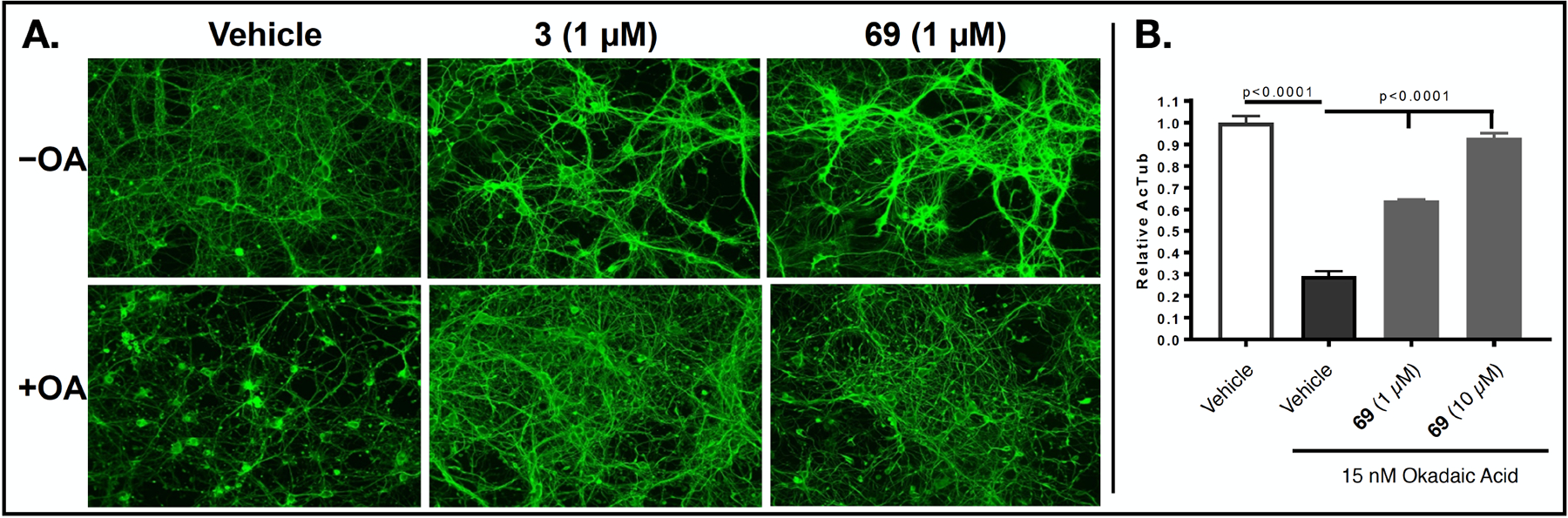
To confirm that the nitrile containing triazolopyrimidine derivatives identified in these studies can stabilize neuronal MTs under conditions of tau loss-of-function, we examined the ability of representative compound, 69, to prevent the MT collapse that occurs from reduced binding of hyperphosphorylated tau to axonal MTs after treatment of neuron cultures with the phosphatase inhibitor, okadaic acid (OA). A. Primary rat cortical neurons treated with 1 μM reference compound 3, or 69 in the absence of OA (−OA) show increased axonal acetyl-tubulin staining relative to those receiving vehicle only. Upon treatment with OA (+OA) in the absence of compound (Vehicle), there is a dramatic reduction in axonal AcTub staining with fragmentation of MTs and neuronal processes (also see11). Co-addition of 3 or 69 (1 μM) with OA results in normalization of AcTub staining and axonal processes. B. ELISA determination of AcTub levels in homogenates from primary mouse cortical neurons treated with 1 or 10 μM of 69, or vehicle, in the presence of OA. The higher concentration of 69 resulted in AcTub levels comparable to those in neurons without OA treatment.
