Figure 3. Basic concept of interpretation of LC-MS/MS spectra.
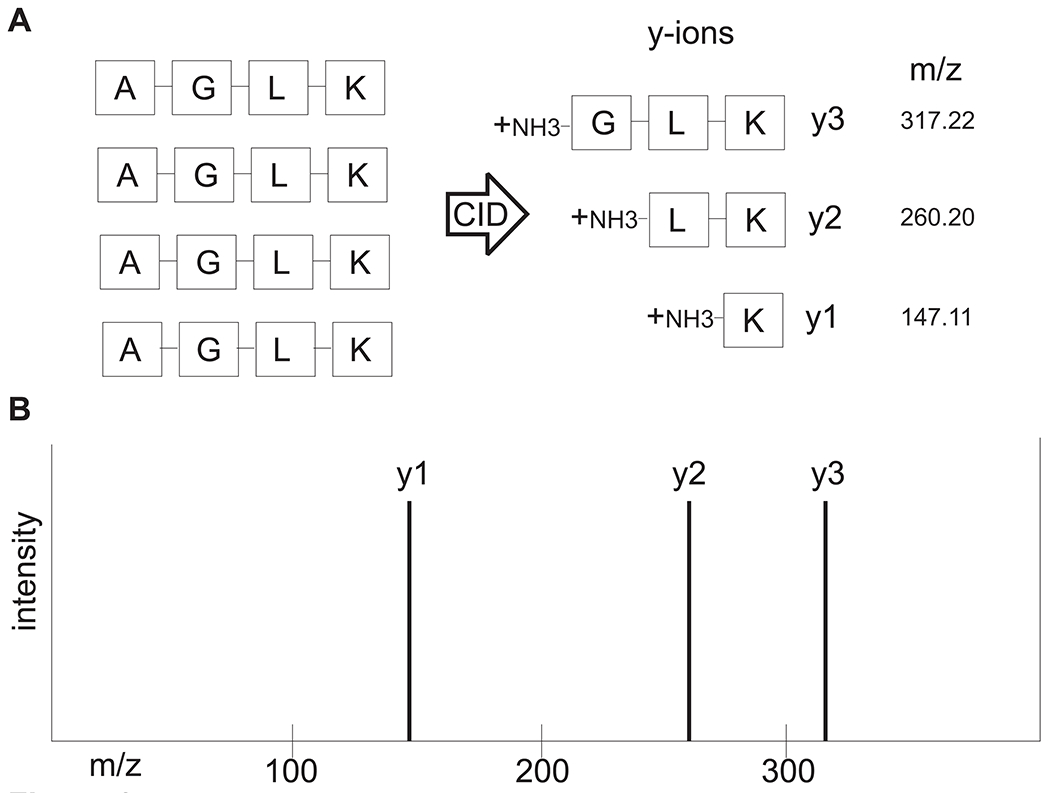
(A) A precursor peptide consisting of amino acids Alanine-Glycine-Leucine-Lysine is fragmented by CID into b and y ions with mass-to-charge ratios (m/z). For the sake of simplicity, only y ions resulting from CID are shown. The aa sequence can now be deduced from the idealized ladder of y ions, as shown in (B). The mass difference between y3 and y2 is 57.02 (which is the residue mass of glycine), and the mass difference between y2 and y1 is 113.09 (which is the residue mass of leucine).
