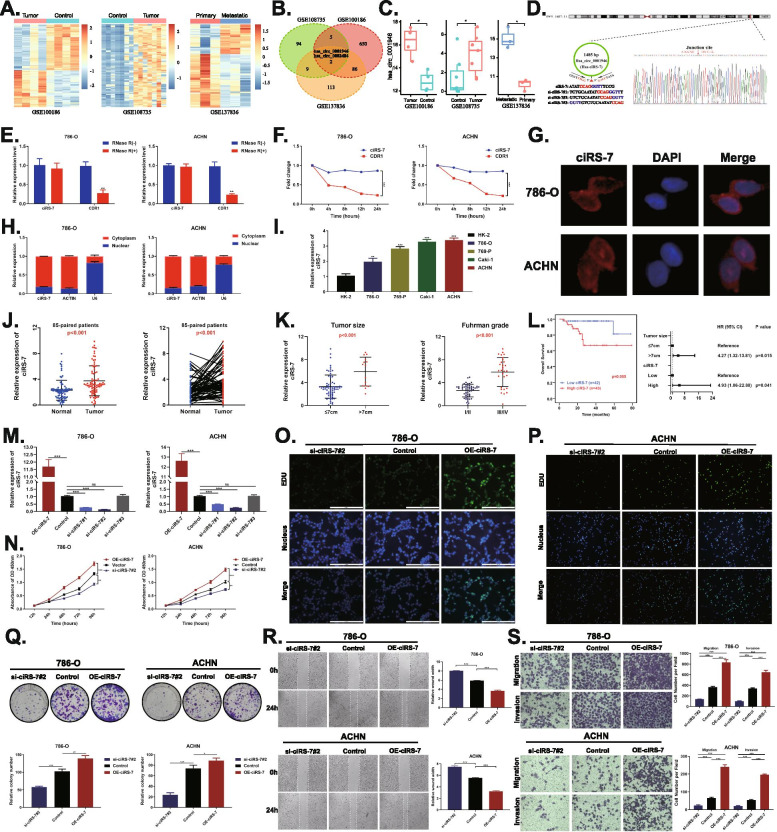
Fig. 1.
ciRS-7 is overexpressed in RCC tissues and cells and promotes RCC cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. A, Hierarchical clustering analysis of differentially expressed circRNAs in GSE100186, GSE108735 and GSE137836. B. Venn diagram of circRNAs commonly highly expressed in GSE100186, GSE108735 and GSE137836. C. Expression of ciRS-7 in GSE100186, GSE108735 and GSE137836. D. Sanger sequencing to verify the splice junctions of ciRS-7. E and F. qRT-PCR analysis of ciRS-7 and linear CDR1 in 786-O and ACHN cells treated with RNase R or actinomycin D. G. FISH assay to detect the cellular localization of ciRS-7. H. qRT-PCR analysis of ciRS-7 was conducted in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of 786-O and ACHN cells. I and J. ciRS-7 was highly expressed in RCC cell lines and tumour tissues. K. Relative expression levels of ciRS-7 in different tumor sizes and Fuhrman grade. L. Kaplan-Meier’s survival curves showed the correlations between ciRS-7 expression and OS, and multivariate Cox regression of hazard ratios for RCC OS. M. Relative expression of ciRS-7 was confirmed by qPCR in 786-O and ACHN cell lines transfected with OE-ciRS-7, control, si-ciRS-7#1, si-ciRS-7#2 or si-ciRS-7#3. N. Growth curves of 786-O and ACHN cell lines were measured after transfection with indicated vectors by CCK-8. O and P. Edu assay to detect cell proliferation capacity after transfection with the indicated vectors. Q, Colony formation assay to detect cell migration ability after transfection with the indicated vectors. R. Wound healing assay to detect cell migration ability after transfection with the indicated vectors. S. Transwell assay to detect cell migration and invasion ability after transfection with the indicated vectors. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)