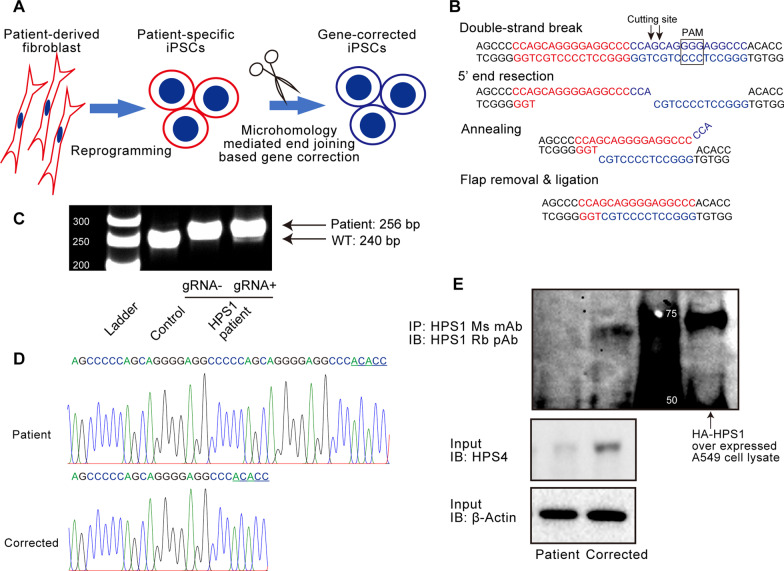
Fig. 1.
Gene correction of 16-bp microduplication in HPS1 patient-specific iPSCs by microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ)-based genome editing. A Overview of the generation of patient-specific iPSCs and their gene-corrected counterparts. B A presumed MMEJ-based repair mechanism of pathogenic 16-bp microduplication. C Genomic PCR of the mutated region in exon 15 of HPS1. Control (healthy donor), 240 bp; HPS1 patient with 16-bp microduplication, 256 bp. Genomic DNA was extracted in bulk from iPSCs transfected with Cas9 and gRNA expression vectors by electroporation. D Sequence data of exon 15 in HPS1 of iPSCs and of those with corrected gene. Gene-corrected iPSCs were selected by a single amplicon of 240 bp after single cell cloning. E Verification of gene repair at the protein level by immunoblot. Immunoprecipitation was performed to detect the full-length of HPS1 protein. A549 cell lysate transfected with HA-HPS1 was used as positive control to detect HPS1