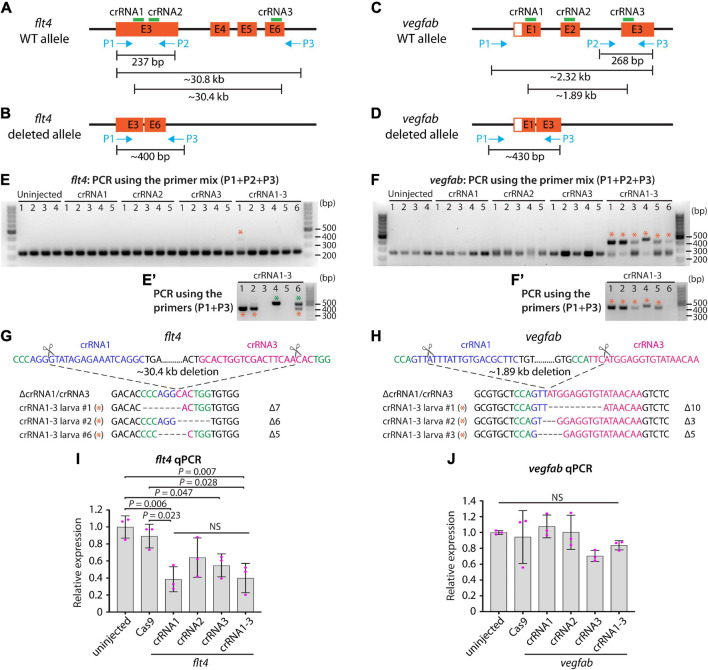
FIGURE 6.
Analysis of large genomic deletions and mRNA decay following cytoplasmic dgRNP injections. (A) Diagram of part of the flt4 genomic locus, indicating approximate locations of the three crRNA target sites and PCR primers. Primer 1 (P1) and primer 2 (P2) were designed to amplify a 237 bp genomic fragment of WT alleles. Primer 3 (P3) was designed far from P1 so these primer pairs cannot efficiently amplify a large genomic fragment (∼30.8 kb) without undergoing genomic deletions (∼30.4 kb) induced by crRNA1 and crRNA3. (B) Diagram of the same part of the flt4 genomic locus after the anticipated genomic deletion (∼30.4 kb) induced by simultaneous targeting of crRNA1 and crRNA3. This genomic deletion is expected to enable PCR amplification of approximately 400 bp of the genomic fragment using primers P1 and P3, which flank these two crRNAs’ target sites. (C) Diagram of part of the vegfab genomic locus, indicating approximate locations of the three crRNA target sites and PCR primers. Primer 2 (P2) and primer 3 (P3) were designed to amplify a 268 bp genomic fragment of WT alleles. Primer 1 (P1) was designed far from P3 so these primer pairs cannot efficiently amplify a large genomic fragment (∼2.32 kb) without undergoing genomic deletions (∼1.89 kb) induced by crRNA1 and crRNA3. (D) Diagram of the same part of the vegfab genomic locus after the anticipated genomic deletion (∼1.89 kb) induced by simultaneous targeting of crRNA1 and crRNA3. This genomic deletion is expected to enable PCR amplification of approximately 430 bp of the genomic fragment using primers P1 and P3, which flank these two crRNAs’ target sites. (E, E’) Genomic DNA from uninjected larvae and those injected with the dgRNPs containing indicated flt4 crRNAs was amplified with the triple primer mix (P1 + P2 + P3; E). Uninjected larvae and those injected with individual crRNAs displayed only a 237 bp WT genomic fragment band. However, the WT band and an additional amplicon (asterisks) expected to be generated from genomic deletion alleles were both detected in the genomes of some F0 larvae injected with the triple dgRNPs. The additional amplicons were detected in more efficient manner with PCR using only the primer pairs (P1 + P3; E’). The bands marked by orange asterisks were detected at the approximate size of 400 bp, whereas those marked by green asterisks were observed at around 500 bp. These bands were cut out and sequenced. (F,F’) Genomic DNA from uninjected larvae and those injected with the dgRNPs containing indicated vegfab crRNAs was amplified with the triple primer mix (P1 + P2 + P3; F). Uninjected larvae and those injected with individual crRNAs displayed only a 268 bp WT genomic fragment band. However, the WT band and an additional amplicon (asterisks) expected to be generated from genomic deletion alleles were both detected in the genomes of all F0 larvae injected with the triple dgRNPs. The additional amplicons were detected at the approximate size of 430 bp with PCR using only the primer pairs (P1 + P3; F’). These bands were cut out and sequenced. (G) Sequence analysis of the PCR products indicated by orange asterisks in (E’) from the triple flt4 dgRNP-injected larvae. The sequence indicated by ΔcrRNA1/crRNA3 represents expected perfect end joining after simultaneous flt4 crRNA1 and crRNA3 gene targeting. The number of base pairs that were apparently deleted from this perfect end joining of predicted cleavage sites is indicated. crRNA1 and crRNA3 target sites are indicated in blue and pink, respectively, along with their PAM sequences (green). (H) Sequence analysis of the PCR products indicated by orange asterisks in (F’) from the triple vegfab dgRNP-injected larvae. The sequence results from the larvae #1–3 are presented. The sequence indicated by ΔcrRNA1/crRNA3 represents expected perfect end joining after simultaneous vegfab crRNA1 and crRNA3 gene targeting. The number of base pairs that were apparently deleted from this perfect end joining of predicted cleavage sites is indicated. crRNA1 and crRNA3 target sites are indicated in blue and pink, respectively, along with their PAM sequences (green). (I) qPCR analysis of flt4 mRNA expression levels in 26 hpf embryonic samples of the indicated treatments. Triple dgRNP-injected samples showed significantly reduced flt4 mRNA levels compared to uninjected and Cas9 injected controls. n = 3 biologically independent samples. (J) qPCR analysis of vegfab mRNA expression levels in 26 hpf embryonic samples of the indicated treatments. No significant difference in vegfab mRNA levels was observed across the groups. n = 3 biologically independent samples. For qPCR analyses (I,J), uninjected expression levels were set at 1. A one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was used to calculate P values.