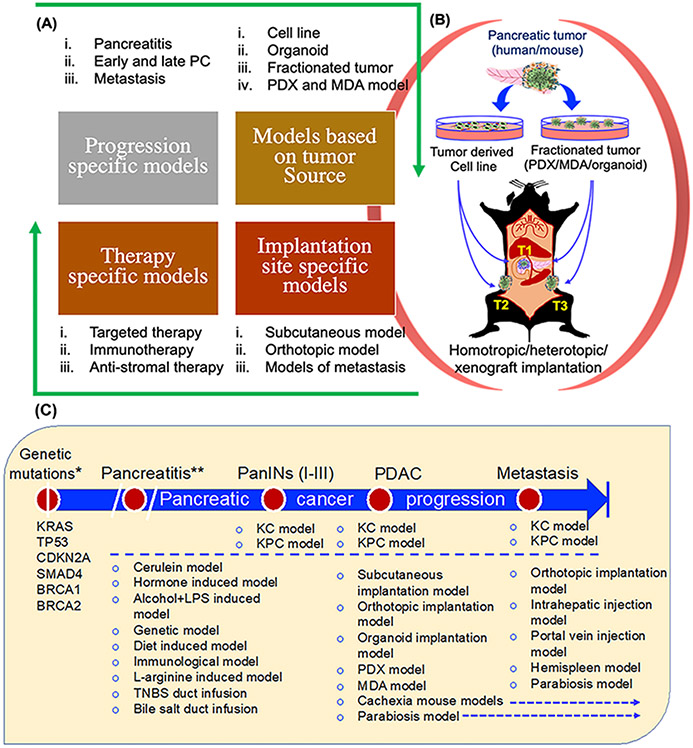
Figure 2. Classification of murine models of PDAC based on various parameters.
Experimental models are classified based on different parameters including, progression stages, implantation source, implantation site, and therapeutic approaches. (A) Murine models based on progression stages include early and late PDAC and metastasis, including pancreatitis as a major risk factor (Top; left panel); models based on implantation material (Top; right panel), and site of implantation (Bottom; right panel). Lastly, therapy-specific models are described to highlight that based on therapy-specific requirements, models for immunotherapy, anti-stromal therapies, and other targeted therapies can be categorized (Bottom; left panel). (B) Illustration of implantation models based on tumor source and implantation site. Different PDAC sources including cell lines/organoids/PDXs/MDAs derived from tumors of the mouse or human pancreas are implanted surgically into the pancreas or injected subcutaneously. (C) PDAC progression stage-specific experimental mouse models. Experimental models are categorized based on different stages of pancreatic cancer progression. Following oncogenic mutations (Listed below the genetic mutations, which is the first event in PDAC progression), PDAC begins with PanIN lesions and progresses to PDAC with primary tumor and distant metastasis. Pancreatitis is included as a major risk factor for PDAC and based on some reports that suggest the development of PDAC from pancreatitis. In addition to selective models for targeted therapy, spontaneous KC and KPC models are shown in all the stages of PDAC progression. PanIN: pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia; PDX: Patient-derived xenograft; MDA: Mouse-derived allograft. *Mutant KRAS is reported as driver mutation with others as complementary mutations. **Pancreatitis is not an essential early event for PDAC but is considered as an important risk factor.