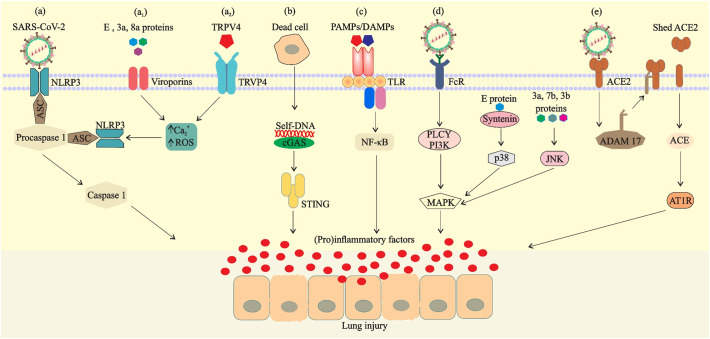
Fig. 5.
Possible mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-mediated inflammatory responses. a) NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) is activated by virus, Ca2+ influx or ROS (induced via viroporins (a1) or TRPV4 (a2)) and binds to the precursor of caspase-1 (procaspase-1) through the adaptor protein ASC in the cell to form a multiprotein complex, thereby activating caspase-1. b) Entry of danger-associated molecular pattern (self- DNA) into the cytoplasm from the nucleus of mitochondria or dead cells activates the cGAS–STING pathway. c) Binding of viral PAMPs/DAMPs to the TLRs and activation of transcription factors for inducing proinflammatory factors. d) Viral structural proteins or binding of virus-Ab complex to FcR can also activate proinflammatory responses via MAPK signaling. e) Binding of the spike protein to ACE2 induces ADAM 17 activity, thereby reducing the number of ACE2 expressed on the cell surface.