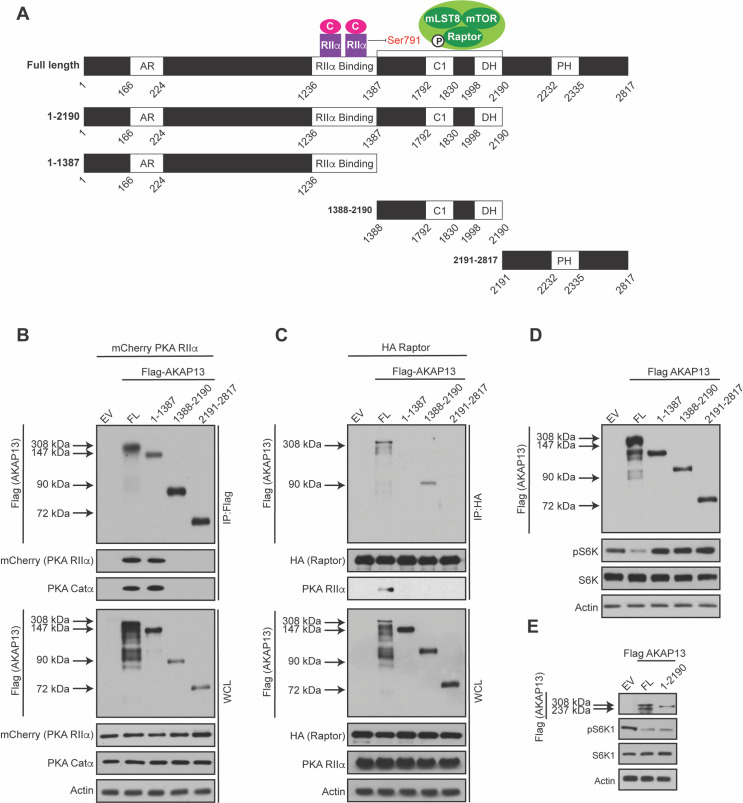
Fig 2. AKAP13 scaffolds PKA and mTORC1 in close proximity.
(A) Schematic of the different Flag-tagged AKAP13 truncations generated for experiments. In addition, an illustration of how the PKA holoenzyme (PKA Catα and PKA RIIα subunits) and mTORC1 bind to AKAP13 according to the results shown below. (B) PKA Catα and PKA RIIα subunits interact with AKAP13. mCherry-tagged PKA RIIα was co-expressed with either empty vector (EV), Flag-tagged AKAP13 full-length (FL), or different Flag-tagged AKAP13 truncations (1–1387, 1388–2190, 2191–2817). 24 hours later Flag immunoprecipitates (IPs) were analyzed by immunoblotting for Flag-tagged AKAP13 FL or truncations, mCherry-tagged PKA RIIα, and PKA Catα. Actin was used as a loading control. WCL denotes whole cell lysate. (C) Raptor interacts with AKAP13 between amino acids 1388 and 2190. HA-tagged Raptor was co-expressed with either empty vector (EV), Flag-tagged AKAP13 full-length (FL), or different Flag-tagged AKAP13 truncations (1–1387, 1388–2190, 2191–2817). 24 hours later HA immunoprecipitates (IPs) were analyzed by immunoblotting for Flag-tagged AKAP13 FL or truncations, HA-tagged Raptor, or PKA RIIα. Actin was used as a loading control. WCL denotes whole cell lysate. (D) Elevated full-length AKAP13 levels decrease mTORC1 activity. Empty vector (EV), Flag-tagged AKAP13 full-length (FL), or different Flag-tagged AKAP13 truncations (1–1387, 1388–2190, 2191–2817) were overexpressed in HEK293A cells for 24 hours. mTORC1 activity was analyzed by protein immunoblotting for the phosphorylation status of S6K1 (pS6K1). S6K and Actin were probed as loading controls. (E) The region of AKAP13 that contains the PKA holoenzyme and mTORC1 regulates mTORC1 activity. Empty vector (EV), Flag-tagged AKAP13 full-length (FL), or Flag-tagged AKAP13 amino acids 1–2190 (1–2190) were overexpressed in HEK293A cells for twenty-four hours. mTORC1 activity was analyzed by protein immunoblotting for the phosphorylation status of S6K1 (pS6K1). S6K and Actin were probed as loading controls.