Table 5.
Activation free energies for the radical dissociation of pyridyl radical 2 to pyridine 4 (Figures1 and2)
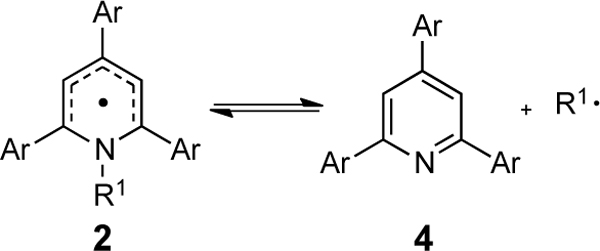
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| calc ΔG‡rdb | Expt ΔG‡rdc | ||||
| (kcal/mol) | |||||
| Entry | Ar | σ a | R1 = i-Pr | R1 = Cy | R1 = Cy |
| 1 | 4-MeOC6H4, 2a | –0.27 | 15.9 | 17.7 | 18.0 |
| 2 | 4-MeC6H4, 2b | –0.17 | 16.5 | 18.2 | 18.4 |
| 3 | Ph, 2c | 0.00 | 17.3 | 18.5 | 18.8 |
| 4 | 4-FC6H4, 2d | 0.06 | 16.9 | 18.3 | 18.5 |
| 5 | 4-CF3C6H4, 2e | 0.54 | 17.5 | 19.0 | 19.0 |
| 6 | 3,5-F2C6H3, 2f | 0.68d | 17.4 | 19.1 | nde |
| 7 | 3,5-Me2C6H3, 12g | – | nd | nd | 18.7 |
Hammett σp parameters for substituents.
Gibbs free energies of activation computed using UM06/6–311+G(d,p), SMD: DMF // UB3LYP/6–31G(d).
Experimental ΔG‡rd obtained from rate constants using the Eyring equation.
For 3,5-difluoro substitution, the σ parameter was estimated additively as a sum of two fluorine σm values of 0.34.
Insolubility of this pyridinium salt prevented accurate measurement.
