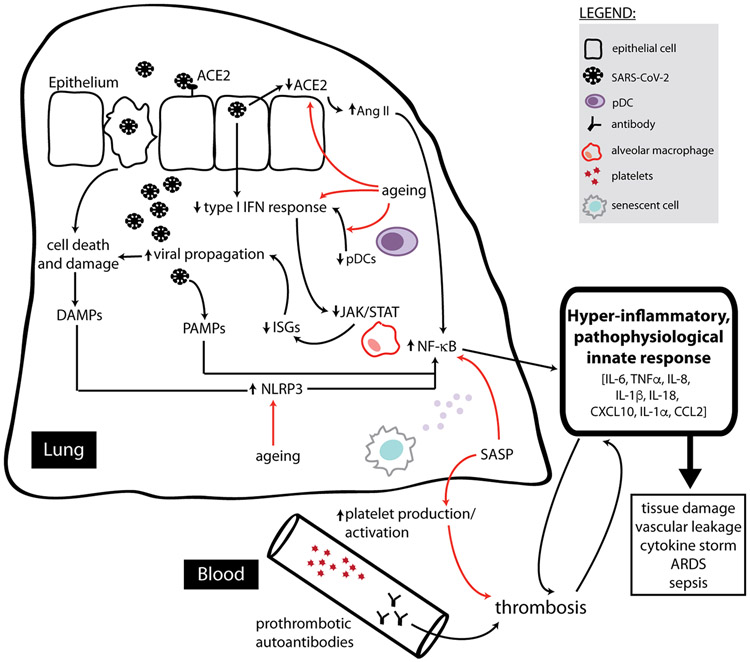
Figure 3. An ageing innate immune system may predispose a patient to severe COVID-19.
Consequences of the virus are indicated by black arrows, while consequences of ageing are indicated by red arrows. SARS-CoV-2 first enters cells by binding to ACE2, and viral entry then leads to the shedding of ACE2. Ageing may also be associated with reduced expression of ACE2, and the low expression of ACE2 after infection potentially mediates a pro-inflammatory state through the production of angiotensin (Ang) II. Severe COVID-19 has also been correlated with reduced type I IFN responses, a defect which may be compounded by aberrant type I IFN signaling with age. This could be made worse by the notable reduction in total number of pDCs found in severe COVID-19 patients. Aged pDCs also have a reduced ability to produce type I IFNs, and the pro-inflammatory nature of the SASP in older individuals desensitizes JAK/STAT signaling in innate immune cells. All of this would compound the loss of type I IFN signaling during severe COVID-19, ultimately leading to reduced expression of antiviral IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) and permitting enhanced viral propagation. This viral replication leads to cell death and damage, causing the production of immunostimulatory DAMPs and PAMPs. Signaling in response to these signals generally activates the NF-κB transcription factor, which is also the main immune signaling pathway engaged by SASP mediatorsand the persistent basal stimulation of pattern recognition receptors in older adults. NF-κB signaling promotes production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. DAMPs linked to both aging and viral infection can also trigger activation of inflammasomes such as NLRP3, potentiating cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-18, as well as triggering further cell death through pyroptosis. SASP mediators and the autoimmune-prone environment associated with aging may also predispose aged individuals to a prothrombotic environment, and thrombosis and inflammation continue to promote one another in a feed-forward loop which further contributes to the hyperinflammatory, pathophysiological innate response that causes devastating outcomes observed in severe COVID-19.