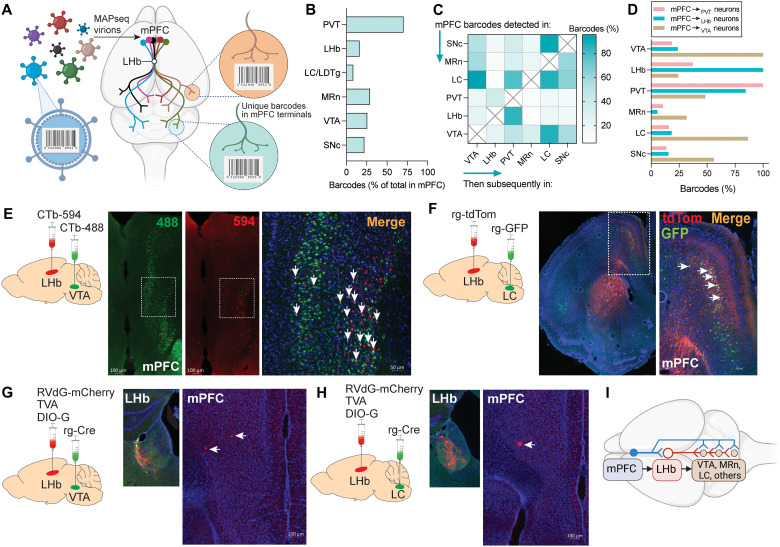
Fig. 3. Connectomes of mPFC➔LHb neurons.
(A) Summary of MAPseq procedure. (B) Percentage of barcodes detected in the mPFC also detected in brain sites listed on y axis. Data were collected from n = 2 mice. (C) Heatmap representation of mPFC barcodes (% total number) detected in brain regions shown on y axis and in regions shown on x axis. (D) Histogram of connectome of mPFC➔PVT, mPFC➔VTA, and mPFC➔LHb neurons. Shown is the distribution of barcodes (%) for mPFC cells that project to the PVT, VTA, and LHb. (E) Summary of injection procedure to label cortical-habenular neurons that project to VTA and fluorescence image of mPFC from mice injected with CTb retrograde tracers in the LHb and VTA. Shown are CTb-594 (red; mPFC➔LHb neurons)–labeled and CTb-488 (green; mPFC➔VTA neurons)–labeled cells. White arrows identify dual-labeled cells (yellow; mPFC➔LHbVTA neurons) in the mPFC. A total of n = 5 mice were imaged. (F) Summary of injection procedure to label cortical-habenular neurons that project to the LC and associated fluorescence image of mPFC from injected mice (red; mPFC➔LHb neurons) and GFP (green; mPFC➔VTA neurons). White arrows identify dual-labeled cells (yellow; mPFC➔LHbLC neurons) in the mPFC. A total of n = 5 mice were imaged. (G) Injection procedure (the tracing the relationship between input and output method, also known as the TRIO method) to label cortico-habenular neurons that project to VTA. Shown are mCherry+ cells in the mPFC, which are cortico-habenular neurons that synapse into LHb neurons that project to VTA. A total of n = 4 mice were imaged. (H) Injection procedure to label cortico-habenular neurons that project to the LC. mCherry+ cells were detected in the mPFC (right), which are cortico-habenular neurons that synapse into LHb neurons that project to the LC. A total of n = 3 mice were imaged. (I) Graphical representation of the cortico-habenular connectome. A population of mPFC neurons (shown in blue) projects concurrently to the LHb and then to the same monoaminergic brain centers to which LHb neurons also project (shown in red).