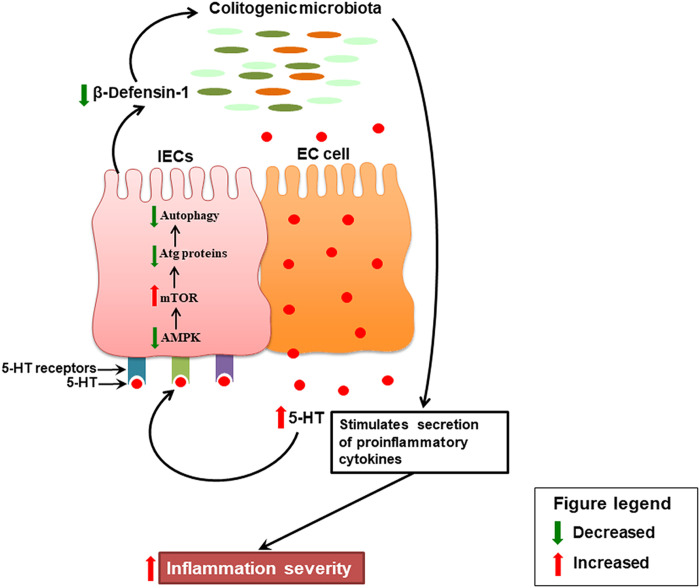
Fig. 10. Schematic representation of the data.
During colitis, increased mucosal 5-HT secreted from the EC cells in the colon binds to 5-HT3, 5-HT4, and 5-HT7 receptors on the IECs and inhibits AMPK. Inhibition of AMPK subsequently activates mTOR. Activation of mTOR inhibits formation of autophagy (Atg) proteins that leads to impairment in autophagy in the IECs. This leads to the reduced production of the antimicrobial peptide, b-defensin-1, by the IECs, which alters the composition of the normal gut microbiota. The colitogenic microbiota stimulates the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-8, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) from IECs and immune cells and, ultimately, exacerbates the severity of inflammation.