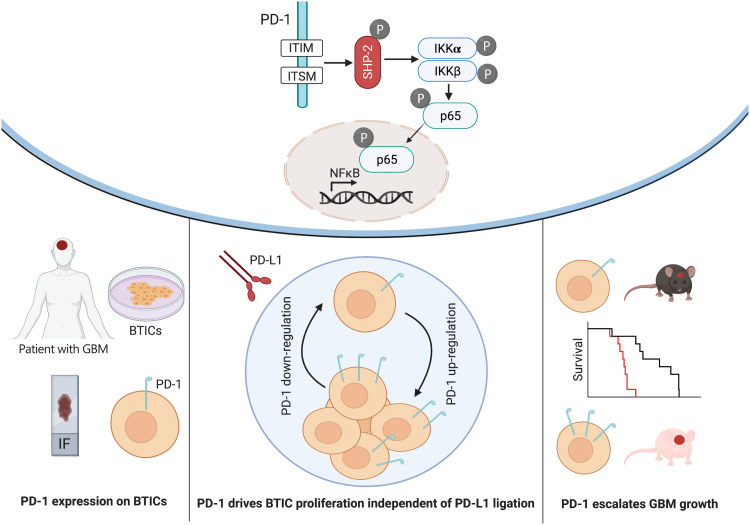
Fig. 8. Diagram of PD-1 expression on BTICs and signaling through NFκB.
PD-1 is expressed on BTICs in resected clinical GBM specimens in situ and patient-derived BTICs in culture. Tumor-promoting effects of PD-1 in BTICs did not require interaction with PD-L1; thus, the therapeutic antibodies were unable to overcome the growth advantage of PD-1 in BTICs. Mice with intracranial Pdcd1 over- or underexpressing BTICs had shorter or longer survival, respectively. Mechanistically, phosphorylation of ITIM and ITSM motifs within the cytoplasmic tail of PD-1 recruited SHP-2 phosphatase and activated the NFκB pathway through IKKα/β in BTICs.