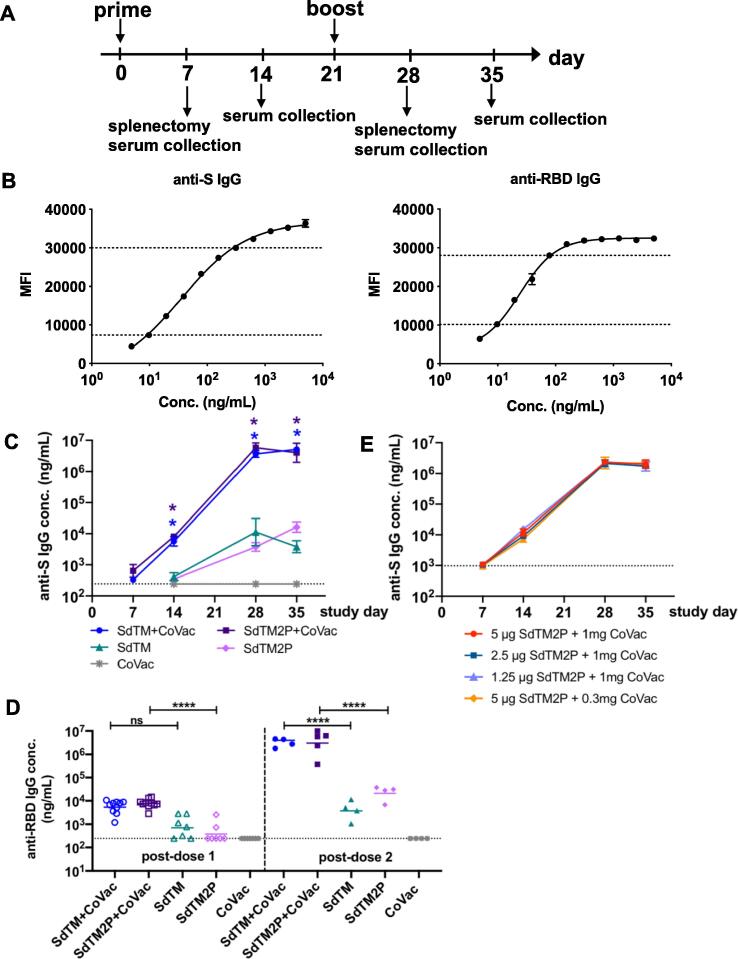
Fig. 1.
IgG antibody responses to recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S proteins. (A) Groups of Swiss Webster mice (n = 7 or 15) were immunized with one or two doses of recombinant S proteins with or without CoVaccine HT™ (CoVac) adjuvant at a 3-week interval. Sera were collected 1 and 2 weeks after each immunization (days 7, 14, 28, and 35), and spleens were harvested 1 week (day 7 and 28) after each immunization. SARS-CoV-2 S-specific IgG titers were measured by a multiplex microsphere immunoassay (MIA) using SdTM2P and RBD-F coupled beads. (B) The purified anti-S antibody was diluted to concentrations in the range of 4.8 to 5000 ng/mL and analyzed by MIA as a standard (as described in the Materials and Methods). Mouse sera were assayed along with the antibody standard and the IgG concentrations was interpolated from the standard curves using a sigmoidal dose–response computer model (GraphPad Prism). The dotted lines denote the top and bottom of linear range that were used to interpolate antibody concentration. (C) The anti-S and (D) anti-RBD antibody titers in sera from mice immunized with SdTM or SdTM2P (purified by hACE2 AC) with or without adjuvants or (E) anti-S antibody in sera of mice administered different dosages (5, 2.5, or 1.25 μg) of SdTM2P (purified by mAb IAC) with adjuvant (1 or 0.3 mg) are expressed as IgG concentrations (ng/mL). The dotted lines in panels C to E indicate the bottom of the linear range of the standard curve. Statistically significant differences in the concentrations of anti-S IgG (panel C) or anti-RBD IgG (panel D) between groups receiving vaccines with or without adjuvant were determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (*p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001).