Figure 4.
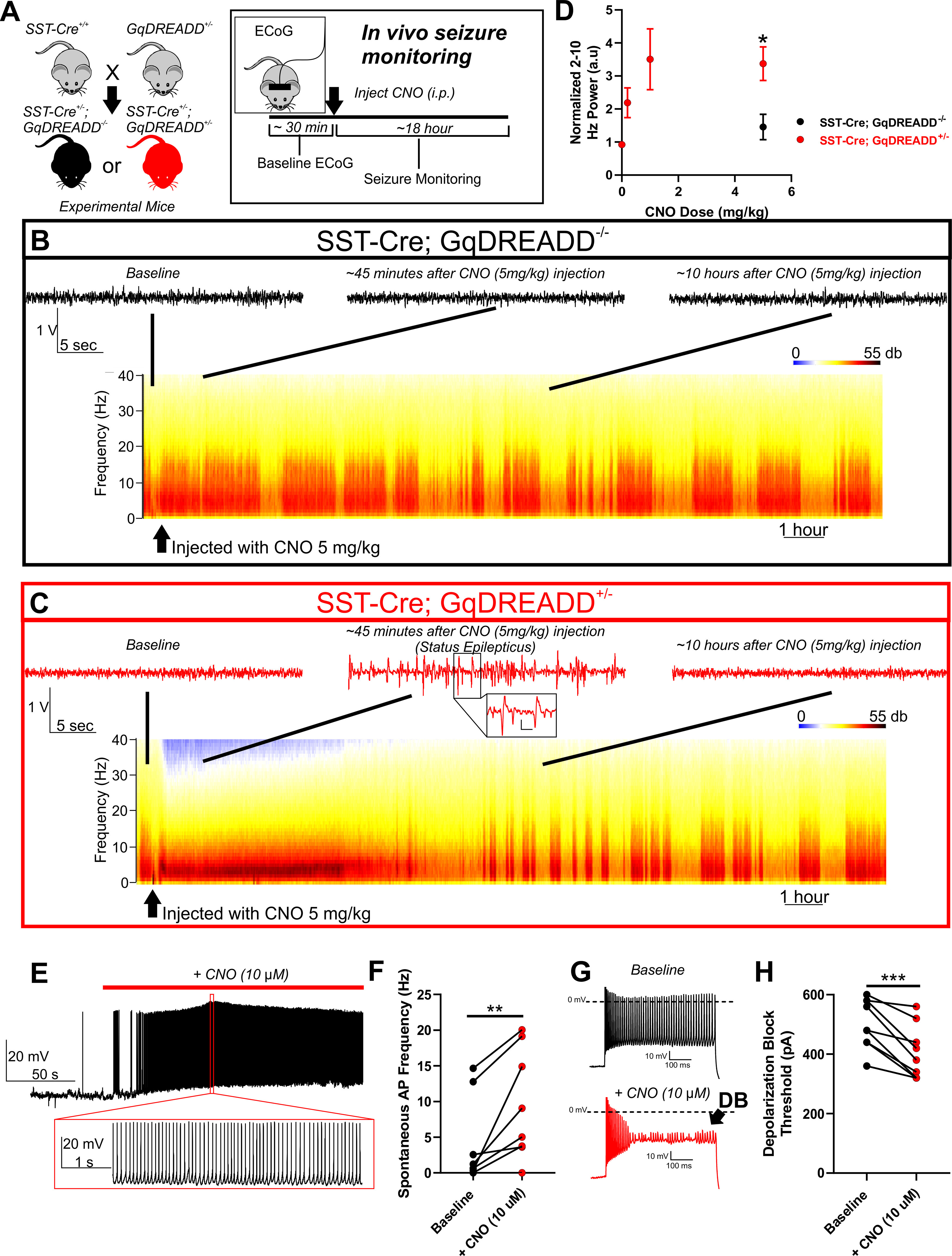
Chemogenetic activation of SST interneurons in WT mice is sufficient to induce seizures. A, Breeding strategy: Female mice homozygous for SST-cre (SST-cre+/+) were bred with male mice heterozygous for a floxed GqDREADD allele (GqDREADD+/−) to produce offspring that were either SST-Cre+/−; GqDREADD−/− control mice (black) or SST-Cre+/−; GqDREADD+/− experimental mice (red). For in vivo seizure monitoring, ECoG was recorded from each mouse for ∼30 min of baseline activity, then treated with vehicle or CNO (i.p. at 0.2, 1, and 5 mg/kg), and monitored for seizure activity for ∼18 h. B, C, Example relative power spectra of ECoG activity for ∼18 h with representative ECoG traces before CNO injection (baseline), ∼45 min after CNO injection, and ∼10 h after CNO injection. B, Example traces indicating that, in mice lacking the GqDREADD receptor (black), CNO treatment (5 mg/kg) did not lead to seizure behavior or changes in ECoG activity. C, Example traces reveal that, on CNO administration, GqDREADD+/− mice (red) exhibited highly synchronized ECoG activity and spike-wave discharges indicative of status epilepticus, which recovers within ∼8 h. Inset, Expanded view of example spike-wave discharges. Calibration: 0.25 V, 0.2 s. D, Normalized 2-10 Hz power relative to pre-injection baseline observed in response to vehicle and CNO (0.2, 1, and 5 mg/kg). SST-Cre; GqDREADD+/− mice (n = 5 for vehicle, 0.2, and 1 mg/kg, n = 8 for 5 mg/kg; red) experienced a robust and dose-dependent increase in 2-10 Hz power. SST-Cre; GqDREADD−/− control mice (black) did not show a significant increase in 2-10 Hz power on administration of 5 mg/kg CNO (n = 4) and was significantly less than SST-Cre; GqDREADD+/− mice. *p < 0.05 (unpaired t test). E, Representative example trace of an SST-Cre; GqDREADD+/− SST interneuron showing spontaneous increase in excitability in response to bath application of CNO (10 μm; red bar). Expanded view illustrates the high firing frequency during CNO exposure. F, Spontaneous firing frequencies of SST interneurons from SST-Cre; GqDREADD+/− mice before (black) and after (red) treatment with CNO (10 μm; n = 8, 4 mice). **p < 0.01 (paired t test). G, Example traces of SST interneuron excitability from an SST-Cre; GqDREADD+/− mouse in response to a 600 pA current injection before (black), and after (red) CNO (10 μm) bath application. Premature depolarization block (DB, arrow) is observed after CNO treatment. H, Depolarization block threshold for each SST-Cre; GqDREADD+/− SST interneuron before (black) and after (red) treatment with CNO (10 μm; n = 8, 4 mice). ***p < 0.001 (paired t test).
