Figure 6.
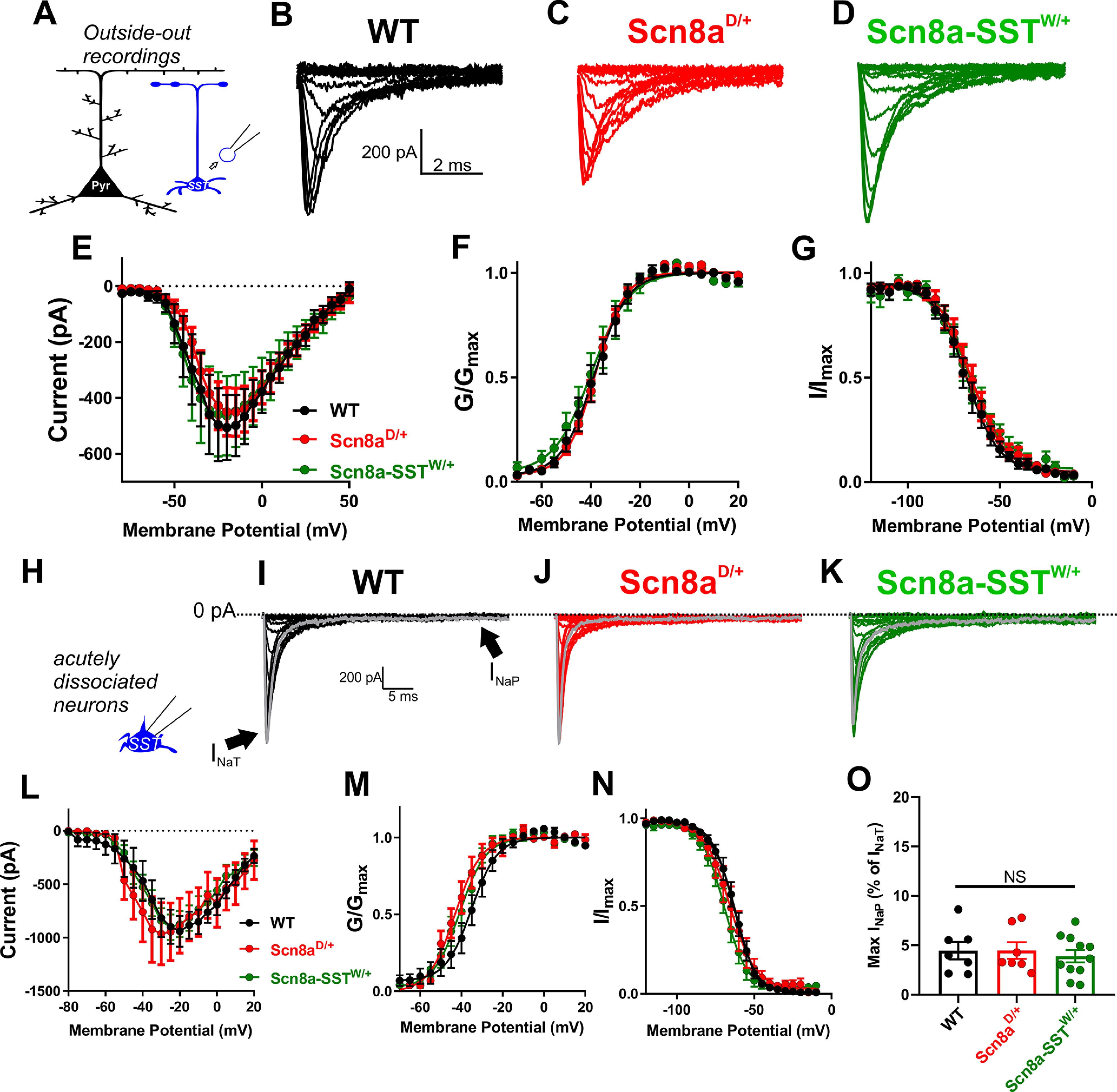
Somatic voltage-gated sodium currents in WT, Scn8aD/+ and Scn8a-SSTW/+ SST interneurons. A, Somatic transient sodium current was assessed in SST interneurons (blue) using patch-clamp recordings in the outside-out configuration. B-D, Example traces for family of voltage-dependent sodium currents recorded from outside-out excised patches from WT (B; black), Scn8aD/+ (C; red), and Scn8a-SSTW/+ (D; green) SST interneurons. E, Current–voltage relationship for WT (black; n = 9, 4 mice), Scn8aD/+ (red; n = 13, 5 mice), and Scn8a-SSTW/+ (green; n = 8, 3 mice) SST interneurons. F, G, Voltage-dependent conductance and steady-state inactivation curves for WT (black), Scn8aD/+ (red), and Scn8a-SSTW/+ (green) SST interneurons. H, Voltage-gated sodium channel currents were also examined in acutely dissociated neurons, which remove much of the distal neuronal processes. I-K, Example traces for family of voltage-dependent sodium currents recorded from acutely dissociated SST interneurons from WT (I; black), Scn8aD/+ (J; red), and Scn8a-SSTW/+ (K; green) mice. Arrows indicate the fast transient (INaT) and persistent (INaP) sodium currents. L, Current–voltage relationship for WT (black; n= 7, 3 mice), Scn8aD/+ (red; n = 7, 3 mice), and Scn8a-SSTW/+ (green; n = 11, 3). M, N, Boltzmann curves for voltage-dependent activation (M) and steady-state inactivation (N). O, Maximum magnitude of the INaP elicited by voltage steps in acutely dissociated SST interneurons.
