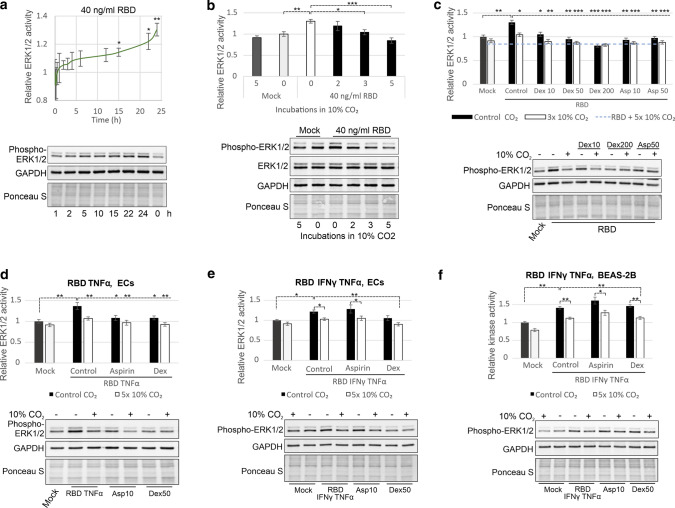
Fig. 3.
RBD-induced ERK1/2 activation can be inhibited by CO2. a Time course of ERK1/2 activation by 40 ng/ml RBD in ECs. b CO2 decreased ERK1/2 activity enhanced by 40 ng/ml RBD in ECs. The indicated number of treatments with 10% CO2 (11 min, a 3-h interval for “3 × CO2” and “5 × CO2” and a 6-h interval for “2 × CO2”) was applied 2 h before collection of ECs and 22 h after RBD administration. c Comparison of the efficiency of ERK1/2 activity inhibition by dex (10, 50 or 200 nM), 10 or 50 μM aspirin (asp) and 10% CO2. ECs were incubated with 40 ng/ml RBD for 16 h. Then, dex and aspirin were applied directly after the first treatment with 10% CO2 (11 min) 8 h before collection of ECs. d–f Efficacy of ERK1/2 inhibition by 10% CO2 (5 treatments, 12 min, 3-h interval), 10 μM aspirin and 50 nM dex. ECs (d–e) or BEAS-2B cells (f) were treated with 40 ng/ml RBD, 10 ng/ml TNFα and/or 7.5 ng/ml IFNγ as indicated for 10 h. Then, specified treatments were applied, and the cells were collected 14 h later. ERK1/2 activity was determined by immunoblotting with an anti-phospho-ERK1/2 antibody, and protein loading was assessed by Ponceau S staining and immunoblotting with anti-GAPDH and anti-ERK1/2 antibodies. The means ± SDs of three independent experiments are presented