Figure 1. Classification of the types of methyl-arginines and protein arginine methyltransferases.
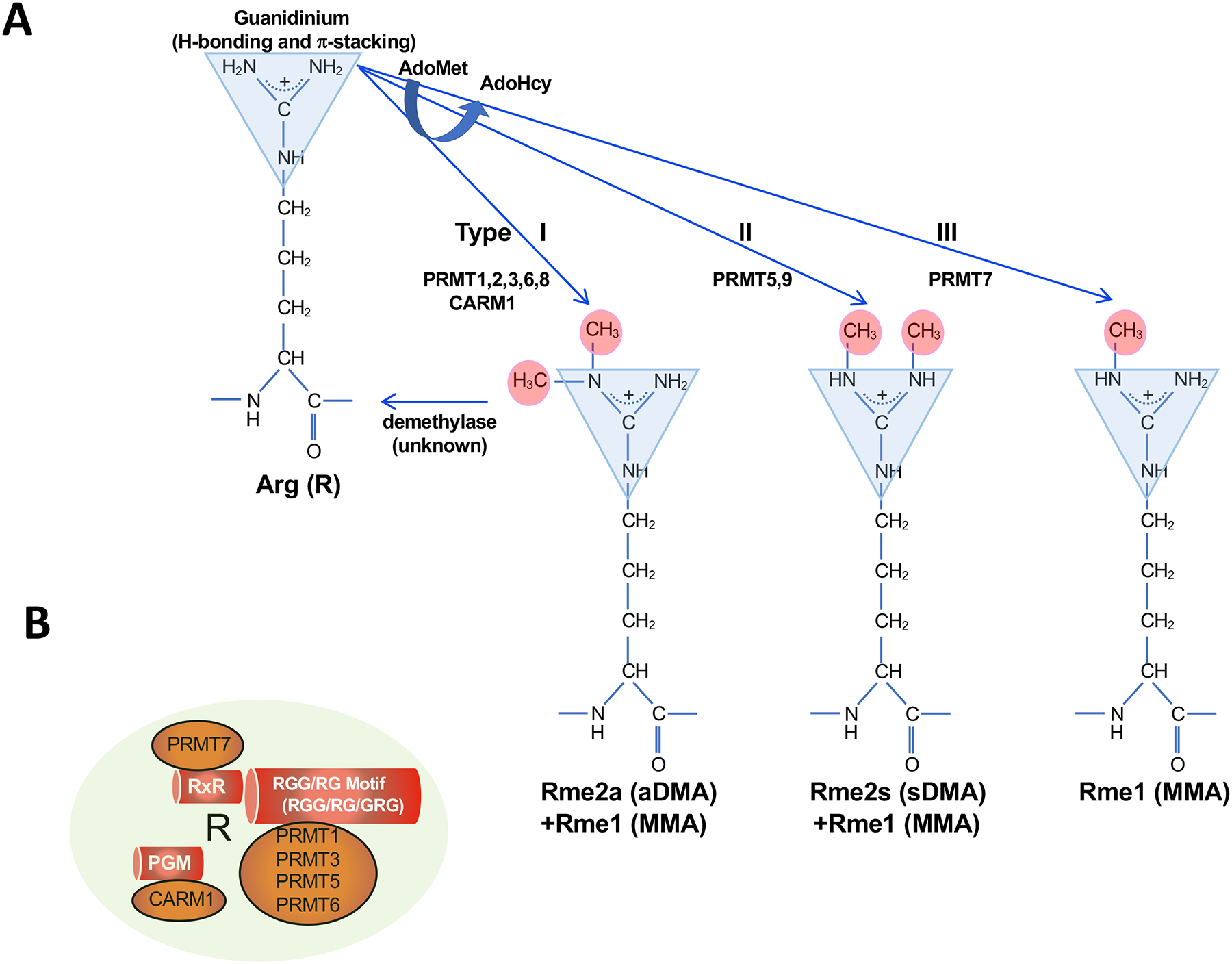
A. Type I and II PRMTs generate monomethyl-arginine (Rme1, MMA) from arginine as a first step, followed by asymmetrical dimethyl-arginine (Rme2a, aDMA; Type I, PRMT1, PRMT2, PRMT3, CARM1, PRMT6 and PRMT8) and symmetrical dimethyl-arginine (Rme2s, sDMA; Type II, PRMT5 and PRMT9) on the guanidino nitrogen atoms using S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) converting it to S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy). The Type III PRMT7 generates only Rme1 (MMA). The guanidinium moiety is shown as a triangle with its H-bonding and π-stacking properties. An arginine demethylase is not known.
B. The known preference of arginine motifs for the PRMTs. PRMT7 has a preference for arginines within the RxR sequences; CARM1 prefers to methylate arginines with neighboring prolines, glycines, and methionines (PGM); PRMT1, PRMT3, PRMT5 and PRMT6 have preference for arginines with neighboring glycines within RGG/RG motifs.
