Figure 4. Arginine methylation negatively regulates the anti-viral response.
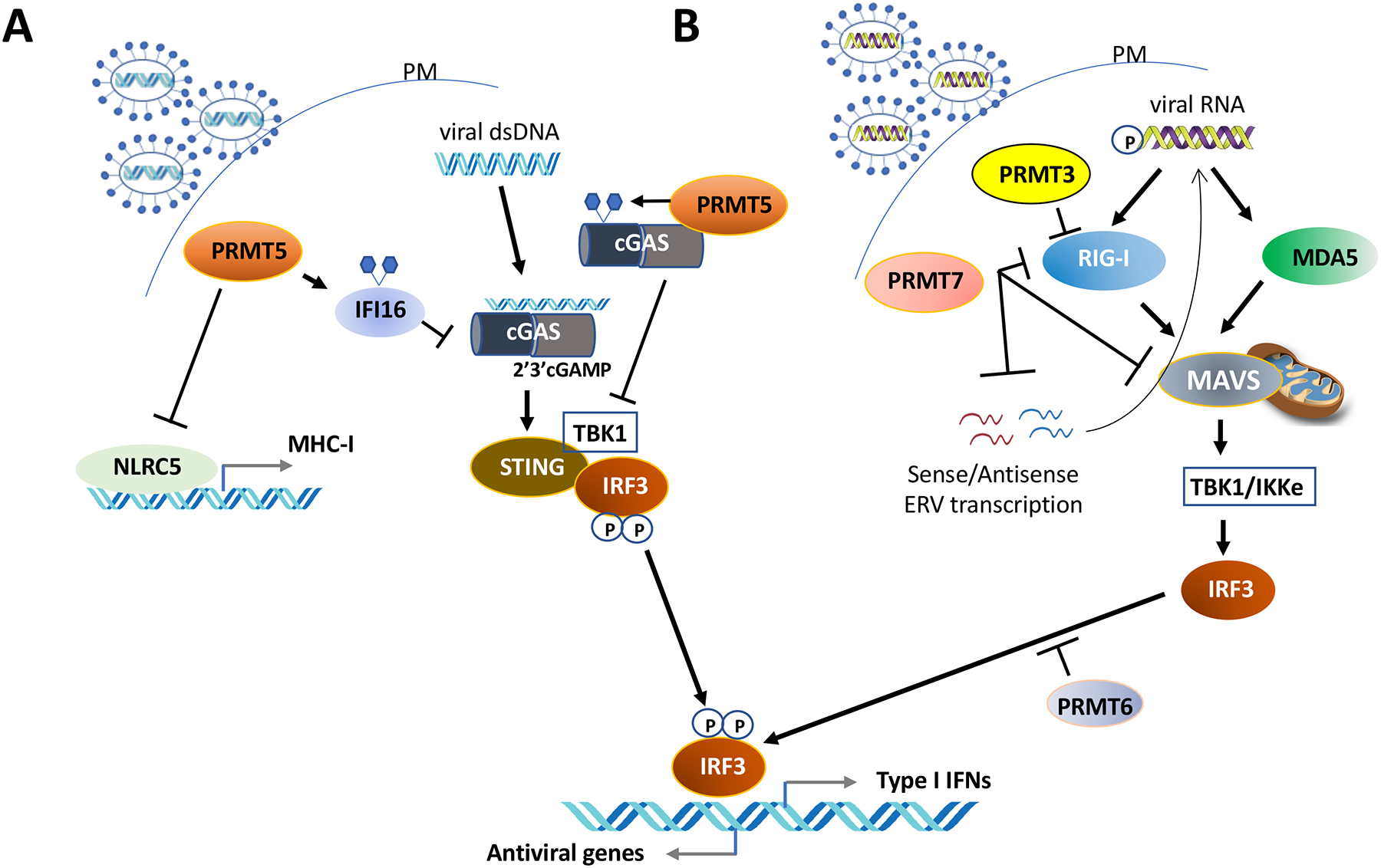
A. Methylation of IFI16 (interferon gamma inducible protein 16) and cGAS (Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase) by PRMT5 inhibits the cGAS/STING (Stimulator of Interferon genes) pathway. PRMT5 also negatively regulates the transcription of NLRC5 (NLR family CARD domain containing 5), a crucial transactivator of MHC (major histocompatibility complex) class genes.
B. PRMT7 inhibits RIG-I-like receptors (retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors, RLRs), MDA5 (melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5), MAVS (mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein) and dsRNA ERV (Endogenous retrovirus) repetitive sequences to inhibit RIG-I signaling. PRMT3 and PRMT6 also inhibit this pathway preventing IRF-3 (Interferon regulatory factor 3) induced type I interferons.
