Figure 1. Electrophysiological profile of iPSC-derived neurons from control and Dup15q subjects during in vitro development.
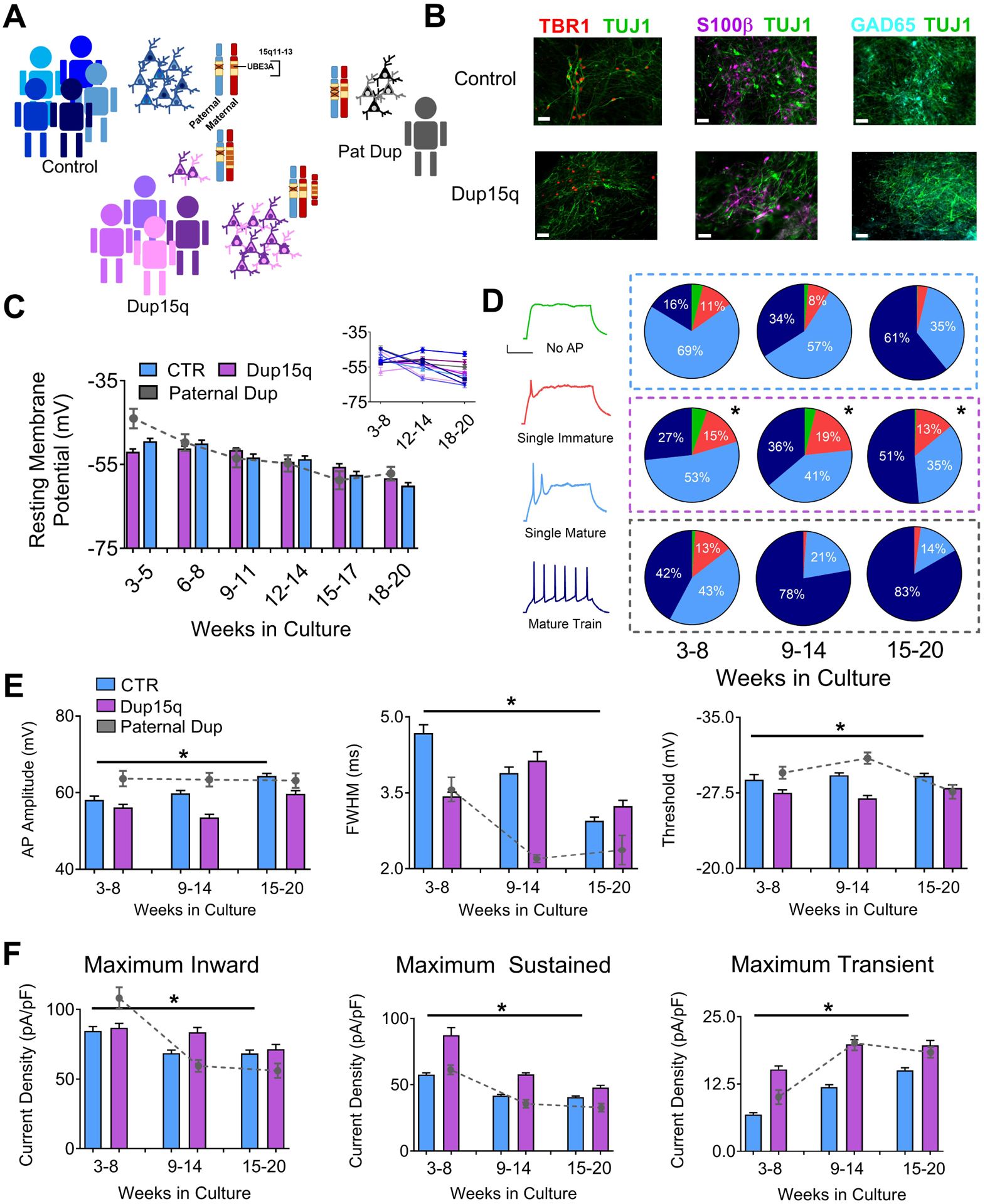
(A) Schematic of patient line genetics of the chromosome 15q11–13 genomic locus. (B) Immunocytochemical staining for TBR1/TUJ1, S100β/TUJI, and GAD65/TUJ1, in control and Dup15q-derived cultures between 20 and 25 weeks in culture. Scale bar, 50 μm (C) Group data for resting membrane potential (RMP) of control (CTR; 5 subjects; n>200 at each time point), Dup15q (4 subjects; n>175 at each time point) and a subject with a paternal duplication of chromosome 15q11-q13 (Paternal Dup; 1 subject; n=45 at each time point) during development. Inset: RMP for all individual lines. For each time bin, n≥30 for all lines. (D) Left: Example traces representing four AP firing patterns used for characterization. Scale bar, 20 mV, 200 ms. Right: Distribution of AP firing patterns for control (blue box; 5 subjects; n>430 at each time point), Dup15q (purple box; 4 subjects; n>430 at each time point), and a 15q11-q13 paternal duplication (grey box; 1 subject; n>60 at each time point) neurons at three developmental time bins. *P<0.0001 for differences between control and Dup15q; χ2 test. #P<0.0001 for differences between control and paternal duplication; χ2 test. (E) AP amplitude (left), full width at half-maximum amplitude (FWHM; middle), and AP threshold (right), for control, Dup15q, and paternal duplication cultures at three time points (n>350 for both control and dup15q at all time points; n>80_for paternal duplication at all time points). *P<0.001 for significant differences between control and Dup15q, #P<0.001 for significant differences between control and paternal duplication (two-way ANOVA). (F) Group data for maximum inward current density (left), maximum sustained outward current density (middle), and maximum transient outward current density (right), for control, Dup15q, and paternal duplication cultures at three time points (n>350 for both control and dup15q at all time points; n>80_for paternal duplication at all time points). *P<0.001 for significant differences between control and Dup15q, #P<0.001 for significant differences between control and paternal duplication (two-way ANOVA).
