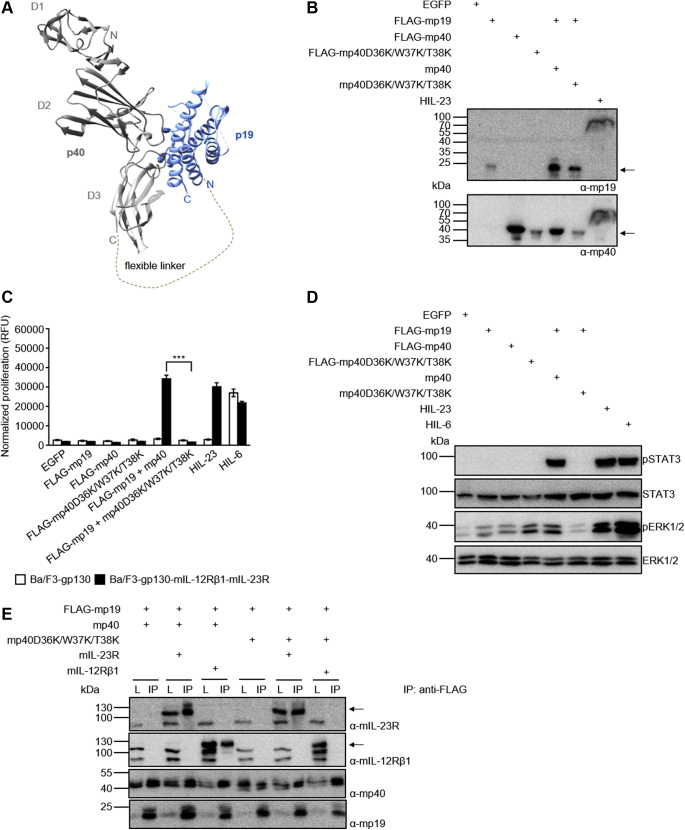
Figure 4.
Murine p40 with D36K/W37K/T38K substitutions interacts with murine p19 but not with murine IL-12Rβ1.A, structure of hIL-23 extracted from the structure of the IL-23:IL-23R complex structure (PDB 5mzv). A flexible linker sequence connecting p40 and p19 is indicated. B, Western blot analysis of secreted murine HIL-23, mp19 and mp40 variants from transfected CHO-K1 cells. The position of mp19 and mp40 variants is indicated by arrows. C, cellular proliferation of Ba/F3-gp130-mIL-12Rβ1-mIL-23R cells. The cells were cultured for 3 days in the presence of 10 ng/ml HIL-6 or with the indicated cytokines (10% conditioned cell culture supernatant of transfected CHO-K1 cells). Parental Ba/F3-gp130 cells were used as controls. The results of one representative experiment of three are shown. Error bars represent S.D. for technical replicates. Statistical analysis used a one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni correction (n = 3), ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001. D, analysis of STAT3 and ERK1/2 activation. Ba/F3-gp130-mIL-12Rβ1-mIL-23R cells were washed, starved, and stimulated with the indicated cytokines (10% conditioned cell culture supernatant of transfected CHO-K1 cells) for 30 min. Cellular lysates were prepared, and equal amounts of total protein (50 μg/lane) were loaded on SDS-PAA gels, followed by immunoblotting using specific antibodies for phospho-STAT3, STAT3, phospho-ERK1/2, and ERK1/2. Western blotting data show results of one representative experiment of two. E, co-IP of FLAG-tagged murine mp19 coexpressed with either mp40 or mp40D36K/W37K/T38K and full-length mIL-12Rβ1 or mIL-23R. The position of mIL-23R and mIL-12Rβ1 is indicated by arrows. One of two independent experiments is shown.