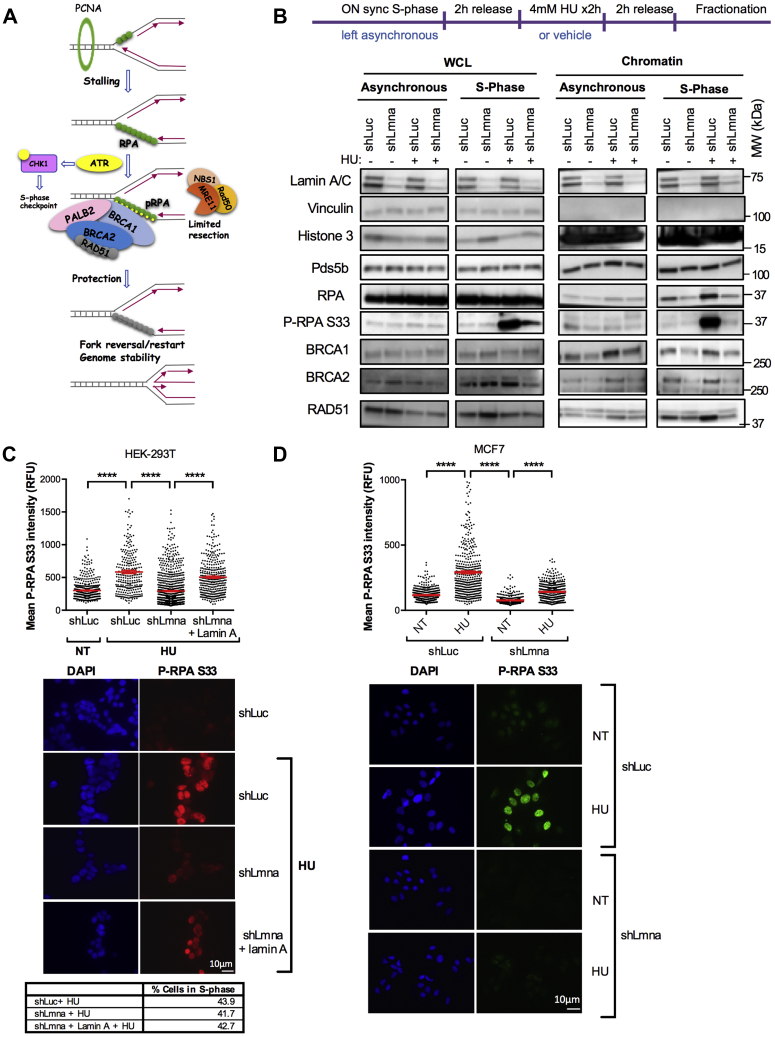
Figure 5.
Lamin A/C deficiency hinders chromatin recruitment and phosphorylation of RPA.A, schematic representation of the events occurring upon stalling of RFs. The uncoupling of the replicative polymerase from the helicase generates ssDNA that is coated by the ssDNA-binding trimeric complex RPA. This activates the ATR/CHK1 intra S-phase checkpoint and ATR-mediated phosphorylation of DNA-bond RPA, which becomes a docking site for a plethora of fork-protective/remodeling factors (BRCA1, PALB2, BRCA2, and RAD51). These factors stabilize the fork and mediate restart of the stalled fork. B, HEK-293T cells proficient (shLuc) and deficient for lamin A/C (shLmna) were either left asynchronous or synchronized in S phase via overnight treatment with 1 μM aphidicholin (APH). Cells were then allowed to recover for 2 h in complete medium, followed by exposure to HU (4 mM) to elicit RS or vehicle as control for 2 h. Subsequently, cells were either lysed directly to prepare whole cell lysates (WCLs) or subjected to subcellular fractionation to isolate the chromatin fraction. Immunoblots show global protein levels from WCL or chromatin-bound proteins from asynchronous and S-phase–synchronized shLuc and shLmna cells. Note how loss of lamin A/C results in a reduction of proteins associated with S-phase chromatin under conditions of RS. Vinculin is the loading control for WCL, whereas Pds5b and H3 are loading controls for the chromatin fraction. Representative immunoblots of three biological repeats. C, immunofluorescence (IF) performed in HEK-293T lamin A/C-proficient (shLuc) and lamin A/C-deficient (shLmna) cells, as well as in cells in which lamin A expression was reconstituted (shLmna + lamin A), and treated with HU to induce RS. Monitored levels of P-RPAS33, a marker of RS that indicates binding of RPA to chromatin and phosphorylation by AKT. Representative fields of cells are shown in the images, and quantification of fluorescence intensity (relative fluorescence units) is shown in the graph (ImageJ program). DAPI staining was used to demarcate nuclei. Results are from two independent experiments, and >200 cells quantified per condition each time. Graph shows each individual value of all measurements from two replicates. The bar indicates the average for those two replicates ± SEM. The table shows percentage of cells in S phase by FACS. D, lamin A/C-proficient and lamin A/C-deficient MCF-7 cells were processed for IF as in (C) to monitor the levels of P-RPAS33 in response to HU treatment. Note the marked decrease in fluorescence intensity in lamin A/C-deficient cells compared with control. Results are from two independent experiments. Graph shows each individual value of all measurements from two replicates. The bar indicates the average for those two replicates ± SEM. ATR, ataxia telangiectasia–mutated and Rad3-related kinase; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; HEK-293T, human embryonic kidney 293T cells; HU, hydroxyurea; RF, replication fork; RS, replication stress.