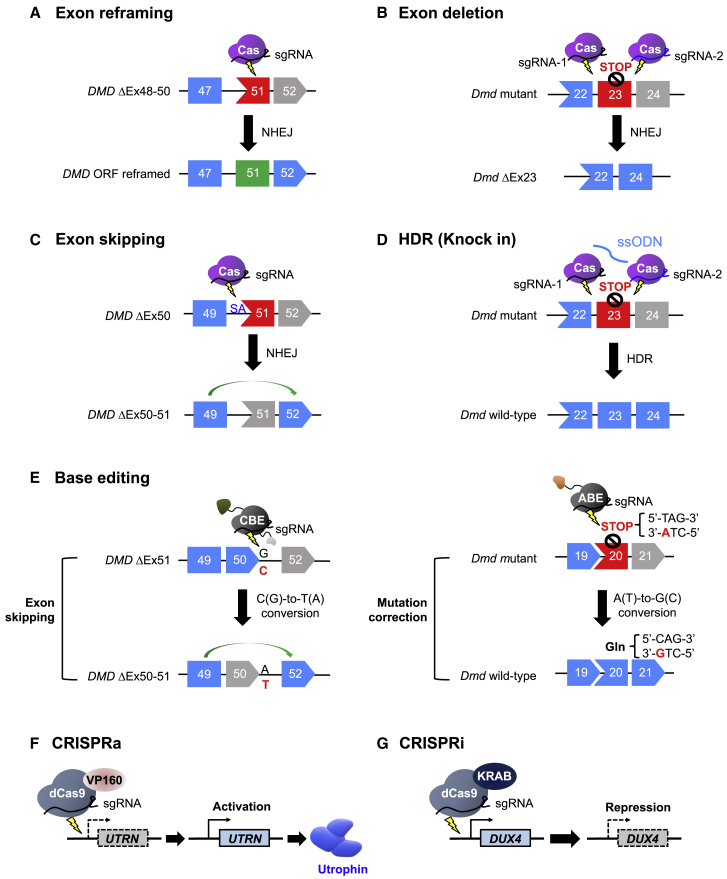
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of CRISPR-mediated genome editing to correct mutations in the DMD gene or ameliorate the effects of such mutations
(A) Exon reframing induced by NHEJ. Small indels that are generated upstream of the premature stop codon in DMD exon 51 have a 1 in 3 probability of reframing the ORF. (B) Exon deletion using 2 sgRNAs targeting intronic regions flanking the mutated Dmd exon 23. (C) DMD exon 51 skipping induced by disruption of a splice acceptor (SA) site to juxtapose exons 49 and 52 in the mRNA and reframed the ORF. (D) Precise, HDR-mediated mutation correction using Cas9, 2 guide RNAs targeted to sites flanking the mutated Dmd exon 23, and ssODNs. (E) Base editor-mediated exon skipping using a CBE or mutation correction using an ABE. (F) CRISPRa-mediated epigenetic editing to upregulate utrophin expression. (G) CRISPRi-mediated epigenetic editing to inhibit DUX4 expression.