Figure 2:
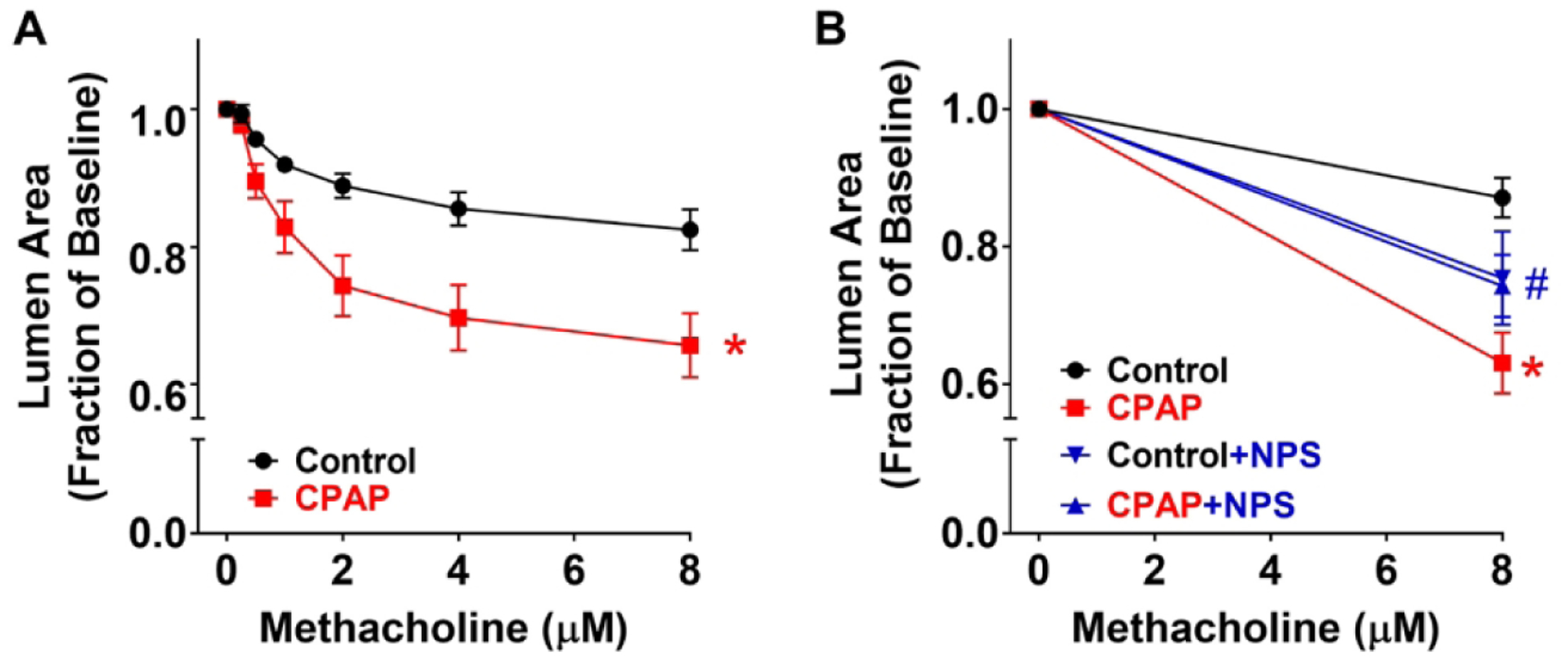
Effect of CPAP and CaSR inhibition on airway responses to methacholine challenge in P21 day old WT mice. In precision cut lung sections from mice exposed to 7 days of CPAP, there was higher reactivity to methacholine compared to control mice at P21 days (A). However, in slices incubated with the CaSR inhibitor, NPS 2143 for 1 hr prior, such CPAP-induced differences were substantially blunted (B). Values are expressed as fraction of baseline lumen size. The smaller lumen size at increasing concentration to methacholine signifies increased AW reactivity.* indicates significant difference (p<0.05) between Ctrl and CPAP, # indicates significant NPS effect (p<0.05) (three-way ANOVA with repeated measures). N=7–10 airways from 4–5 mice/group.
